- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買(mǎi)賣(mài)IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄1916 > DS34S132GN+ (Maxim Integrated Products)IC TDM OVER PACKET 676-BGA PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | DS34S132GN+ |
| 廠(chǎng)商: | Maxim Integrated Products |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 121/194頁(yè) |
| 文件大小: | 0K |
| 描述: | IC TDM OVER PACKET 676-BGA |
| 產(chǎn)品培訓(xùn)模塊: | Lead (SnPb) Finish for COTS Obsolescence Mitigation Program |
| 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)包裝: | 40 |
| 功能: | TDM-over-Packet(TDMoP) |
| 接口: | TDMoP |
| 電路數(shù): | 1 |
| 電源電壓: | 1.8V, 3.3V |
| 工作溫度: | -40°C ~ 85°C |
| 安裝類(lèi)型: | 表面貼裝 |
| 封裝/外殼: | 676-BGA |
| 供應(yīng)商設(shè)備封裝: | 676-PBGA(27x27) |
| 包裝: | 管件 |
| 其它名稱(chēng): | 90-34S13+2N0 |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)第21頁(yè)第22頁(yè)第23頁(yè)第24頁(yè)第25頁(yè)第26頁(yè)第27頁(yè)第28頁(yè)第29頁(yè)第30頁(yè)第31頁(yè)第32頁(yè)第33頁(yè)第34頁(yè)第35頁(yè)第36頁(yè)第37頁(yè)第38頁(yè)第39頁(yè)第40頁(yè)第41頁(yè)第42頁(yè)第43頁(yè)第44頁(yè)第45頁(yè)第46頁(yè)第47頁(yè)第48頁(yè)第49頁(yè)第50頁(yè)第51頁(yè)第52頁(yè)第53頁(yè)第54頁(yè)第55頁(yè)第56頁(yè)第57頁(yè)第58頁(yè)第59頁(yè)第60頁(yè)第61頁(yè)第62頁(yè)第63頁(yè)第64頁(yè)第65頁(yè)第66頁(yè)第67頁(yè)第68頁(yè)第69頁(yè)第70頁(yè)第71頁(yè)第72頁(yè)第73頁(yè)第74頁(yè)第75頁(yè)第76頁(yè)第77頁(yè)第78頁(yè)第79頁(yè)第80頁(yè)第81頁(yè)第82頁(yè)第83頁(yè)第84頁(yè)第85頁(yè)第86頁(yè)第87頁(yè)第88頁(yè)第89頁(yè)第90頁(yè)第91頁(yè)第92頁(yè)第93頁(yè)第94頁(yè)第95頁(yè)第96頁(yè)第97頁(yè)第98頁(yè)第99頁(yè)第100頁(yè)第101頁(yè)第102頁(yè)第103頁(yè)第104頁(yè)第105頁(yè)第106頁(yè)第107頁(yè)第108頁(yè)第109頁(yè)第110頁(yè)第111頁(yè)第112頁(yè)第113頁(yè)第114頁(yè)第115頁(yè)第116頁(yè)第117頁(yè)第118頁(yè)第119頁(yè)第120頁(yè)當(dāng)前第121頁(yè)第122頁(yè)第123頁(yè)第124頁(yè)第125頁(yè)第126頁(yè)第127頁(yè)第128頁(yè)第129頁(yè)第130頁(yè)第131頁(yè)第132頁(yè)第133頁(yè)第134頁(yè)第135頁(yè)第136頁(yè)第137頁(yè)第138頁(yè)第139頁(yè)第140頁(yè)第141頁(yè)第142頁(yè)第143頁(yè)第144頁(yè)第145頁(yè)第146頁(yè)第147頁(yè)第148頁(yè)第149頁(yè)第150頁(yè)第151頁(yè)第152頁(yè)第153頁(yè)第154頁(yè)第155頁(yè)第156頁(yè)第157頁(yè)第158頁(yè)第159頁(yè)第160頁(yè)第161頁(yè)第162頁(yè)第163頁(yè)第164頁(yè)第165頁(yè)第166頁(yè)第167頁(yè)第168頁(yè)第169頁(yè)第170頁(yè)第171頁(yè)第172頁(yè)第173頁(yè)第174頁(yè)第175頁(yè)第176頁(yè)第177頁(yè)第178頁(yè)第179頁(yè)第180頁(yè)第181頁(yè)第182頁(yè)第183頁(yè)第184頁(yè)第185頁(yè)第186頁(yè)第187頁(yè)第188頁(yè)第189頁(yè)第190頁(yè)第191頁(yè)第192頁(yè)第193頁(yè)第194頁(yè)
DS34S132 DATA SHEET
19-4750; Rev 1; 07/11
32 of 194
9.2 TDM Port Functions
The S132 includes 32 TDM Ports. Each TDM Port can be used to support a T1, E1 or any slower TDM data
stream. Each TDM Port uses a serial clock and data interface. The high level functions include:
Structured & Unstructured Formats
T1, E1 and slower TDM Port Line Rates
T1SF, T1ESF and E1 Multi-frame Formats
N x 64 Kb/s PW Packet Payload Rates
With & without CAS Signaling
DS0 Timeslot Assignment
CPU Monitor and Control of CAS Signaling
CPU Control for Data Conditioning
TDM Port Timing
From Recovered or External Time References
Adaptive & Differential Clock Recovery
Generates Differential & Absolute Timestamps
TDM Port, Timeslot and PW Loopbacks
BERT Diagnostics
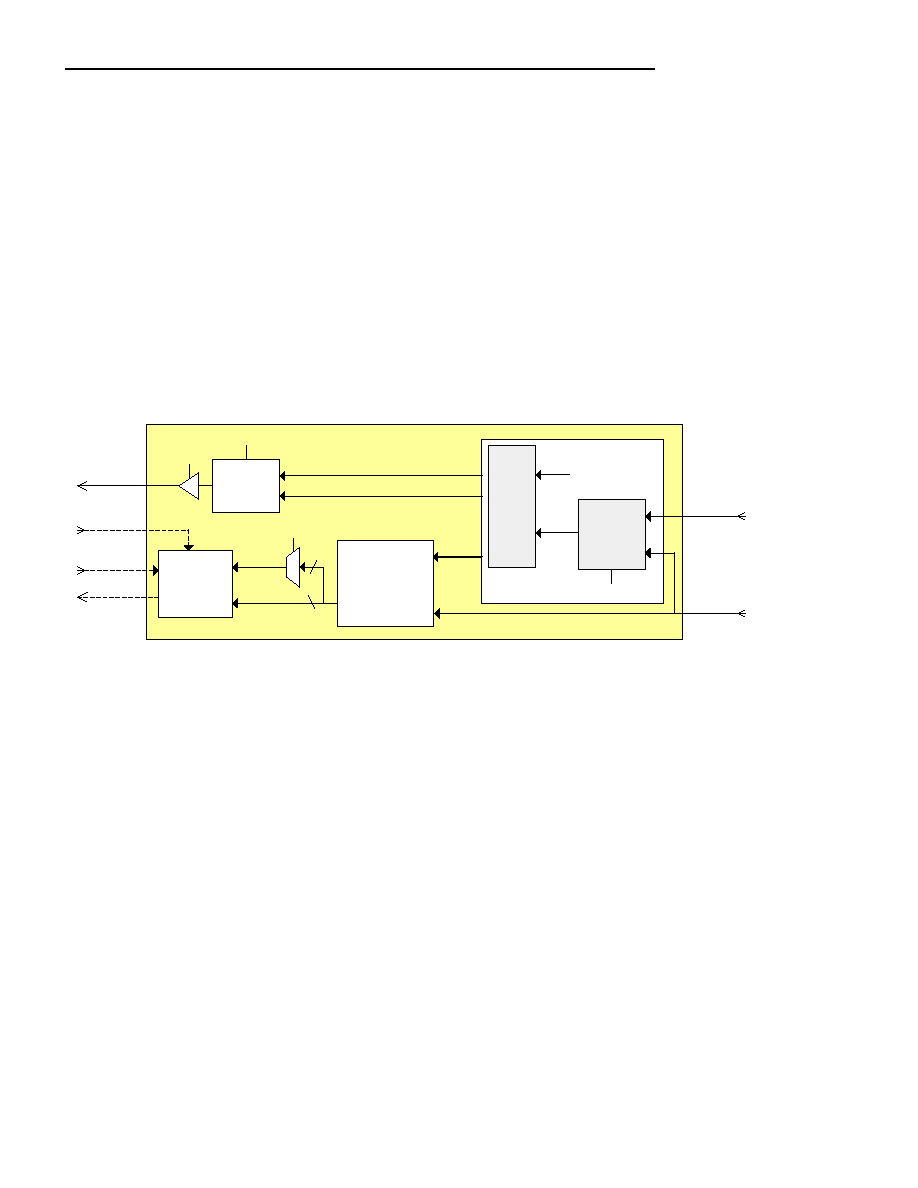
9.2.1 TDM Port Related Input and Output Clocks
The TDM Port Input and Output Clocks are identified in Figure 9-7.
Figure 9-7. TDM Port Input and Output Clock Overview
DS34S132
CLAD
Ck
Select
Freq
Synthesizer
CLAD
Clock
Select
1.544 MHz
synclk
REFCLK
LIUCLK
2.048 MHz
LCS
LCE
SCS
32 Clock
Recovery
Engines
TDM
Port n
(n = 1 - 32)
EXTCLK0
EXTCLK1
RCLKn
TCLKOn
aclk_n
grclk
32
GRCSS
32
Freq Select
FS[3:0]
CMNCLK
DCR
Common
Clock
High Quality
Reference
(e.g. OCXO)
synclk
_ref_in
The S132 Clock Recovery Engines support “Adaptive Clock Recovery” (ACR) and “Differential Clock Recovery”
(DCR). The ACR technique measures the timing of each successive RXP Packet to determine the recovered clock
frequency. The DCR technique uses RTP timestamps to determine the recovered clock frequency. Two external
clock recovery reference inputs (REFCLK and CMNCLK) are used to supply 1) a Frequency Synthesizer reference
input and 2) to provide a DCR common clock reference.
The Frequency Synthesizer reference input (synclk_ref_in) is required to generate an internal “synclk” signal. To
achieve the jitter/wander performance of ITU G.823/824/8261 the reference should be at least equal to that of a
Stratum 3 clock. The reference can be input on either REFCLK or CMNCLK (selected with G.CCR.SCS). For PSTN
and Cellular Mobile Phone applications, the BITS or GPS Network Timing commonly provide at least a Stratum 3
reference. For applications where a Network Timing reference is not available, then an OCXO may be used. Some
specialized TCXOs can also meet these stringent requirements. Otherwise, if the jitter/wander requirements can be
relaxed then the synclk reference input signal requirements can be equally relaxed.
To support the DCR mode, both ends of the PW must share a common clock reference that is derived from a single
timing source so that the frequency of the common clock reference at both ends of the PW are locked to each
other. The CMNCLK input is used to provide the DCR common clock reference.
In public network applications that use the DCR mode, the public network broadcast Network Timing, that provides
a Stratum 3 or better reference (e.g. BITS or GPS), can be used for the DCR common clock (CMNCLK) input and
the synclk reference input; and the REFCLK input can be tied low to save power.
In applications that use the DCR mode, but the DCR common clock reference is not a Stratum 3 reference (e.g.
private networks), the DCR common clock is connected to the CMNCLK input and a high quality reference (e.g.
OCXO) is connected to the REFCLK input.
In applications that do not use the DCR mode, only a high quality reference is required that can be connected to
CMNCLK or REFCLK and the unused input pin can be tied low to save power.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| DS34T102GN+ | IC TDM OVER PACKET 484TEBGA |
| DS3501U+H | IC POT NV 128POS HV 10-USOP |
| DS3502U+ | IC POT DGTL NV 128TAP 10-MSOP |
| DS3503U+ | IC POT DGTL NV 128TAP 10-MSOP |
| DS3897MX | IC TXRX BTL TRAPEZIODAL 20-SOIC |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| DS34S132GN+ | 功能描述:通信集成電路 - 若干 32Port TDM-Over-Pack Transport Device RoHS:否 制造商:Maxim Integrated 類(lèi)型:Transport Devices 封裝 / 箱體:TECSBGA-256 數(shù)據(jù)速率:100 Mbps 電源電壓-最大:1.89 V, 3.465 V 電源電壓-最小:1.71 V, 3.135 V 電源電流:50 mA, 225 mA 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 最小工作溫度:- 40 C 封裝:Tube |
| DS34S132GNA2+ | 功能描述:通信集成電路 - 若干 32Port TDM-Over-Pack Transport Device RoHS:否 制造商:Maxim Integrated 類(lèi)型:Transport Devices 封裝 / 箱體:TECSBGA-256 數(shù)據(jù)速率:100 Mbps 電源電壓-最大:1.89 V, 3.465 V 電源電壓-最小:1.71 V, 3.135 V 電源電流:50 mA, 225 mA 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 最小工作溫度:- 40 C 封裝:Tube |
| DS34T101 | 制造商:MAXIM 制造商全稱(chēng):Maxim Integrated Products 功能描述:Single/Dual/Quad/Octal TDM-over-Packet Chip |
| DS34T101_08 | 制造商:MAXIM 制造商全稱(chēng):Maxim Integrated Products 功能描述:Single/Dual/Quad/Octal TDM-over-Packet Chip |
| DS34T101_09 | 制造商:MAXIM 制造商全稱(chēng):Maxim Integrated Products 功能描述:Single/Dual/Quad/Octal TDM-over-Packet Chip |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。