- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄223992 > HY27SA081G1M-FPEB (HYNIX SEMICONDUCTOR INC) 128M X 8 FLASH 1.8V PROM, 12000 ns, PBGA63 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | HY27SA081G1M-FPEB |
| 廠商: | HYNIX SEMICONDUCTOR INC |
| 元件分類: | PROM |
| 英文描述: | 128M X 8 FLASH 1.8V PROM, 12000 ns, PBGA63 |
| 封裝: | 8.50 X 15 MM, 1.20 MM HEIGHT, 0.80 MM PITCH, LEAD FREE, FBGA-63 |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 13/45頁(yè) |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 675K |
| 代理商: | HY27SA081G1M-FPEB |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)當(dāng)前第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)第21頁(yè)第22頁(yè)第23頁(yè)第24頁(yè)第25頁(yè)第26頁(yè)第27頁(yè)第28頁(yè)第29頁(yè)第30頁(yè)第31頁(yè)第32頁(yè)第33頁(yè)第34頁(yè)第35頁(yè)第36頁(yè)第37頁(yè)第38頁(yè)第39頁(yè)第40頁(yè)第41頁(yè)第42頁(yè)第43頁(yè)第44頁(yè)第45頁(yè)
Rev 0.3 / May. 2004
20
Preliminary
HY27UA(08/16)1G1M Series
HY27SA(08/16)1G1M Series
1Gbit (128Mx8bit / 64Mx16bit) NAND Flash
Once the erase operation has completed the Status Register can be checked for errors.
Reset
The Reset command is used to reset the Command Interface and Status Register. If the Reset command is issued dur-
ing any operation, the operation will be aborted. If it was a program or erase operation that was aborted, the contents
of the memory locations being modified will no longer be valid as the data will be partially programmed or erased.
If the device has already been reset then the new Reset command will not be accepted. The Ready/Busy signal goes
Low for tBLBH4 after the Reset command is issued. The value of tBLBH4 depends on the operation that the device was
performing when the command was issued, refer to Table 15 for the values.
Read Status Register
The device contains a Status Register which provides information on the current or previous Program or Erase opera-
tion. The various bits in the Status Register convey information and errors on the operation.
The Status Register is read by issuing the Read Status Register command. The Status Register information is present
on the output data bus (I/O0- I/O7) on the falling edge of Chip Enable or Read Enable, whichever occurs last. When
several memories are connected in a system, the use of Chip Enable and Read Enable signals allows the system to poll
each device separately, even when the Ready/Busy pins are common-wired. It is not necessary to toggle the Chip
Enable or Read Enable signals to update the contents of the Status Register.
After the Read Status Register command has been issued, the device remains in Read Status Register mode until
another command is issued. Therefore if a Read Status Register command is issued during a Random Read cycle a
new read command must be issued to continue with a Page Read or Sequential Row Read operation.
The Status Register bits are summarized in Table 6, Status Register Bits. Refer to Table 6 in conjunction with the fol-
lowing text descriptions.
Write Protection Bit (SR7)
The Write Protection bit can be used to identify if the device is protected or not. If the Write Protection bit is set to '1'
the device is not protected and program or erase operations are allowed. If the Write Protection bit is set to '0' the
device is protected and program or erase operations are not allowed.
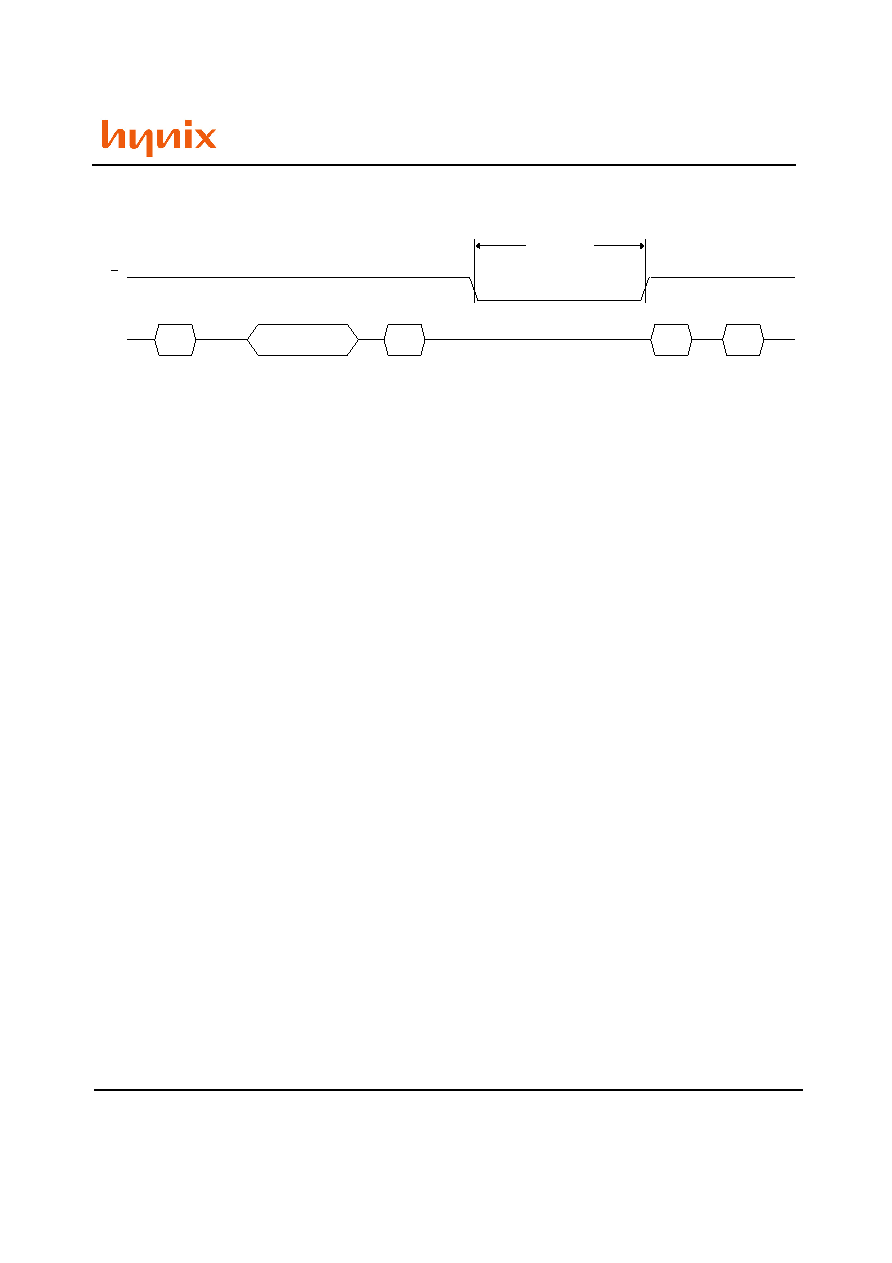
Figure 17. Block Erase Operation
Block Address
Inputs
I/O
60h
Confirm
Code
D0h
SR0
Block Erase
Setup Code
Busy
tBLBH3
(Erase Busy time)
RB
70h
Read Status Register
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| HY27SA081G1M-VPEB | 128M X 8 FLASH 1.8V PROM, 12000 ns, PDSO48 |
| HY27UA081G1M-TIB | 128M X 8 FLASH 3.3V PROM, 12000 ns, PDSO48 |
| HY27US08121B-TPIS | 64M X 8 FLASH 3.3V PROM, 18 ns, PDSO48 |
| HY27US08121B-FIB | 64M X 8 FLASH 3.3V PROM, 18 ns, PBGA63 |
| HY27US081G1MSES | 128M X 8 FLASH 2.7V PROM, 45 ns, PDSO48 |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| HY27SA161G1M | 制造商:HYNIX 制造商全稱:Hynix Semiconductor 功能描述:1Gbit (128Mx8bit / 64Mx16bit) NAND Flash Memory |
| HY27SA1G1M | 制造商:HYNIX 制造商全稱:Hynix Semiconductor 功能描述:1Gbit (128Mx8bit / 64Mx16bit) NAND Flash Memory |
| HY27SAXXX | 制造商:HYNIX 制造商全稱:Hynix Semiconductor 功能描述:1Gbit (128Mx8bit / 64Mx16bit) NAND Flash Memory |
| HY27SF081G2A | 制造商:HYNIX 制造商全稱:Hynix Semiconductor 功能描述:1Gbit (128Mx8bit / 64Mx16bit) NAND Flash |
| HY27SF081G2A-F(P) | 制造商:SK Hynix Inc 功能描述: |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。