- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄367854 > PDI1394L11 (NXP Semiconductors N.V.) 1394 AV Link Layer Controller(AV(音頻/視頻)鏈接層控制器) PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | PDI1394L11 |
| 廠商: | NXP Semiconductors N.V. |
| 英文描述: | 1394 AV Link Layer Controller(AV(音頻/視頻)鏈接層控制器) |
| 中文描述: | 1394影音鏈路層控制器(視聽(音頻/視頻)鏈接層控制器) |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 16/46頁 |
| 文件大小: | 294K |
| 代理商: | PDI1394L11 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁當(dāng)前第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
PDI1394L11
1394 AV link layer controller
1997 Oct 21
16
Table 3. Block Transmit Field
Field Name
Description
spd, tLabel, rt, tCode, destinationID,
destinationOffsetHigh, destinationOffsetLow, rCode
See Table 2.
dataLength
The number of bytes of data to be transmitted in this packet
extendedTcode
The tCode indicates a lock transaction, this specifies the actual lock action to be
performed with the data in this packet.
block data
The data to be sent. If dataLength=0, no data should be written into the FIFO for
this field. Regardless of the destination or source alignment of the data, the first
byte of the block must appear in the high order byte of the first quadlet.
padding
If the dataLength mod 4 is not zero, then zero–value bytes are added onto the end
of the packet to guarantee that a whole number of quadlets is sent.
12.5.1.4
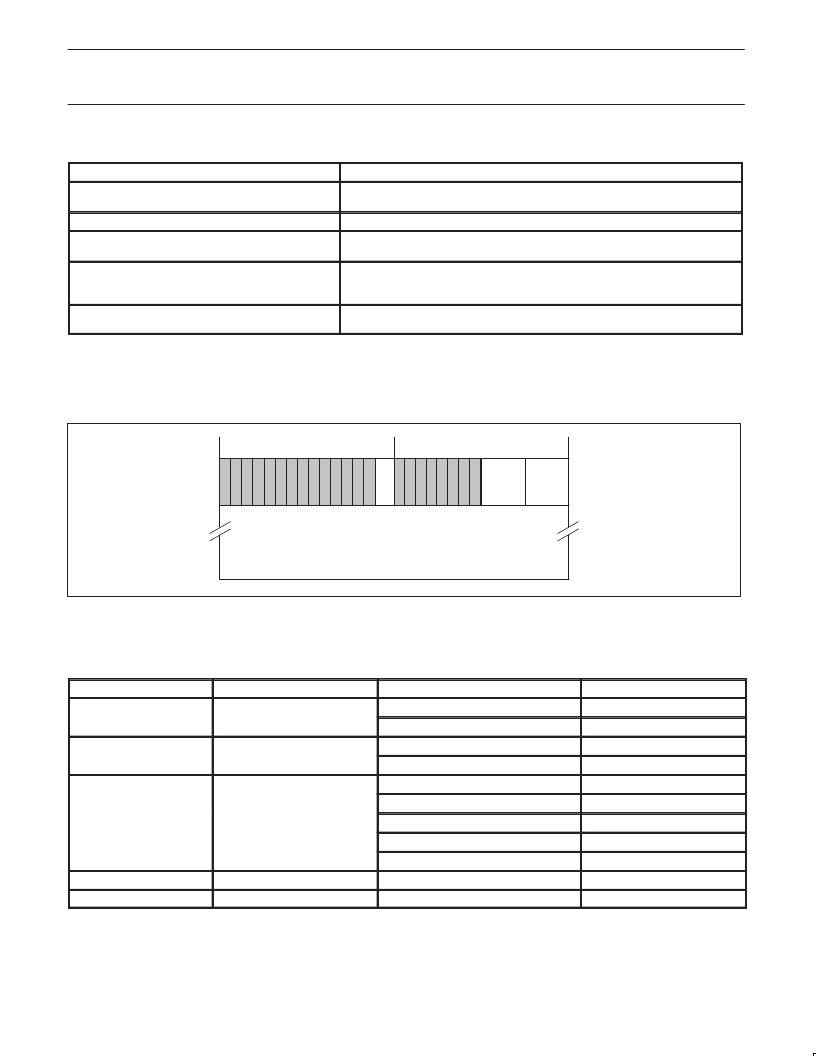
The unformatted transmit format is shown in Figure 11. The first quadlet contains packet control information. The remaining quadlets contain
data that is transmitted without any formatting on the bus. No CRC is appended on the packet, nor is any data in the first quadlet sent. This is
used to send PHY configuration and Link-on packets. Note that the bit-inverted check quadlet must be included in the FIFO since the AV Link
core will not generate it.
Unformatted Transmit
spd
tLabel
1110
0000
29 28 272625 24 23 22 212019 18 1716 15 1413 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
unformatted packet data
SV00256
31 30
Figure 11. Unformatted Transmit Format
12.5.2
This section describes the asynchronous receive packet formats. Four basic asynchronous data packet formats and one confirmation format exist:
Asynchronous Receive Packet Formats
Table 4. Asynchronous Data Packet Formats
ITEM
FORMAT
USAGE
TRANSACTION CODE
1
No packet data
No-packet data
Quadlet read requests
4
Quadlet/block write responses
2
2
Quadlet packet
Qaudlet write requests
0
Quadlet read responses
6
Block read requests
5
Block write requests
1
3
Block Packet
Block read responses
7
Lock requests
9
Lock responses
B
hex
E
hex
8
4
Self-ID / PHY packet
Concatenated self-ID / PHY packets
5
Confirmation packet
Confirmation of packet transmission
Each packet format uses several fields. More information about most of these fields can be found in the 1394 specification.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| PDI1394L21 | Full Duplex AV Link Layer Ccontroller(全雙工AV鏈接層控制器) |
| PDI1394L41 | Content Protection AV Link Layer(內(nèi)容可保護(hù)的AV鏈接層控制器) |
| PDI1394P21 | 3-port Physical Layer Interface(三端口物理層接口) |
| PDI1394P22 | 3-port Physical Layer Interface(三端口物理層接口) |
| PDI1394P24 | 2-port 400 Mbps physical layer interface(2端口 400 Mbps物理層接口) |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| PDI1394L11BA | 制造商:PHILIPS 制造商全稱:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述:1394 AV link layer controller |
| PDI1394L11BA-S | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:IEEE 1394 (Firewire) Bus Interface/Controller |
| PDI1394L21 | 制造商:PHILIPS 制造商全稱:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述:1394 full duplex AV link layer controller |
| PDI1394L21BE | 制造商:PHILIPS 制造商全稱:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述:1394 full duplex AV link layer controller |
| PDI1394L21BP | 制造商:PHILIPS 制造商全稱:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述:1394 full duplex AV link layer controller |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。