- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄98068 > S1C6S460D 4-BIT, MROM, 2 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, UUC124 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | S1C6S460D |
| 元件分類: | 微控制器/微處理器 |
| 英文描述: | 4-BIT, MROM, 2 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, UUC124 |
| 封裝: | 4.69 X 4.68 MM, DIE-124 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 76/107頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 788K |
| 代理商: | S1C6S460D |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁當前第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁第103頁第104頁第105頁第106頁第107頁
62
EPSON
S1C6S460 TECHNICAL MANUAL
CHAPTER 9: SERIAL INTERFACE
9.3 Master Mode and Slave Mode of Serial Interface
The serial interface of the S1C6S460 has two types of operation mode: master mode and slave mode.
In the master mode, it uses an internal clock as synchronous clock of the built-in shift register, generates
this internal clock at the SCLK terminal and controls the external (slave side) serial interface.
In the slave mode, the synchronous clock output from the external (master side) serial device is input
from the SCLK terminal and uses it as the synchronous clock to the built- in shift register.
The master mode and slave mode are selected through registers SCS0 and SCS1; when the master mode is
selected, a synchronous clock may be selected from among 3 types as shown in Table 9.3.1.
Table 9.3.1 Synchronous clock selection
SCS1 SCS0
Mode
Synchronous clock
1
CLK
1
0
Master mode
CLK/2
0
1
CLK/4
0
Slave mode
External clock
CLK : CPU system clock
At initial reset, the slave mode (external clock mode) is selected.
Moreover, the synchronous clock, along with the input/output of the 8 bits serial data, is controlled as
follows:
At master mode, after output of 8 clocks from the SCLK terminal, clock output is automatically
suspended and SCLK terminal is fixed at high level.
At slave mode, after input of 8 clocks to the SCLK terminal, subsequent clock inputs are masked.
Note: When using the serial interface in the master mode, CPU system clock is used as the synchronous
clock. Accordingly, when the serial interface is operating, system clock switching (fOSC1
fOSC3)
should not be performed.
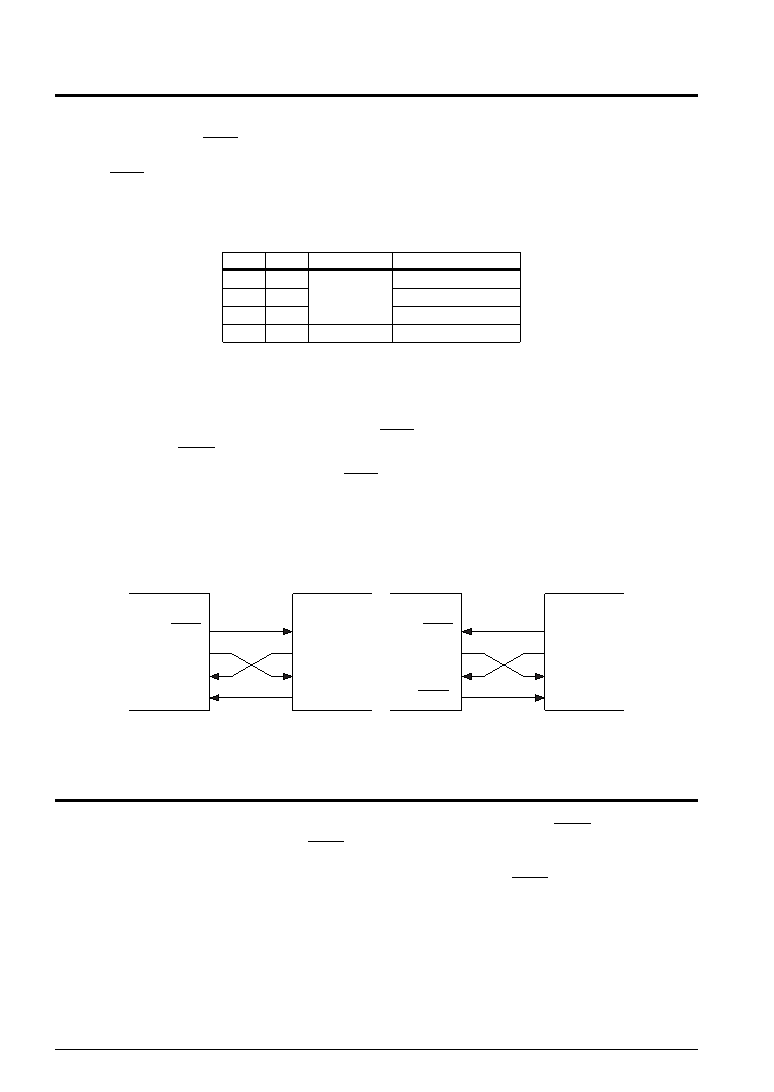
A sample basic serial input/output portion connection is shown in Figure 9.3.1.
S1C6S460
Master mode
Slave mode
SCLK
SOUT
SIN
Input terminal
External
serial device
CLK
SOUT
SIN
READY
S1C6S460
SCLK
SOUT
SIN
R33(SRDY)
External
serial device
CLK
SOUT
SIN
Input terminal
Fig. 9.3.1 Sample basic connection of serial input/output section
9.4 Data Input/Output and Interrupt Function
The serial interface of S1C6S460 can input/output data via the internal 8 bits shift register. The shift
register operates by synchronizing with either the synchronous clock output from SCLK terminal (master
mode), or the synchronous clock input to SCLK (slave mode).
The serial interface generates interrupt on completion of the 8 bits serial data input/output. Detection of
serial data input/output is done by the counting of the synchronous clock (SCLK); the clock completes
input/output operation when 8 counts (equivalent to 8 cycles) have been made and then generates
interrupt.
The serial data input/output procedure data is explained below:
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| S1C88104P0A0100 | 8-BIT, MROM, 8.2 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PBGA240 |
| S1C88317D0A0100 | MICROCONTROLLER, UUC170 |
| S1C88308D0A0100 | MICROCONTROLLER, UUC170 |
| S1C88308F0A0100 | MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP160 |
| S1C88348F | 8-BIT, MROM, 8.2 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP16 |
相關代理商/技術參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| S1C7309X | 制造商:SAMSUNG 制造商全稱:Samsung semiconductor 功能描述:B/W CCD PROCESSOR |
| S1C7309X01 | 制造商:SAMSUNG 制造商全稱:Samsung semiconductor 功能描述:B/W CCD PROCESSOR |
| S1C88349 | 制造商:EPSON 制造商全稱:EPSON 功能描述:8-bit Single Chip Microcomputer |
| S1C88649 | 制造商:EPSON 制造商全稱:EPSON 功能描述:8-bit Single Chip Microcomputer |
| S1C88650 | 制造商:EPSON 制造商全稱:EPSON 功能描述:8-bit Single Chip Microcomputer |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。