- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄45028 > M3455AG8FP 4-BIT, OTPROM, 6 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP52 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | M3455AG8FP |
| 元件分類: | 微控制器/微處理器 |
| 英文描述: | 4-BIT, OTPROM, 6 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP52 |
| 封裝: | 10 X 10 MM, 0.65 MM PITCH, PLASTIC, LQFP-52 |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 108/150頁(yè) |
| 文件大小: | 1818K |
| 代理商: | M3455AG8FP |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)第21頁(yè)第22頁(yè)第23頁(yè)第24頁(yè)第25頁(yè)第26頁(yè)第27頁(yè)第28頁(yè)第29頁(yè)第30頁(yè)第31頁(yè)第32頁(yè)第33頁(yè)第34頁(yè)第35頁(yè)第36頁(yè)第37頁(yè)第38頁(yè)第39頁(yè)第40頁(yè)第41頁(yè)第42頁(yè)第43頁(yè)第44頁(yè)第45頁(yè)第46頁(yè)第47頁(yè)第48頁(yè)第49頁(yè)第50頁(yè)第51頁(yè)第52頁(yè)第53頁(yè)第54頁(yè)第55頁(yè)第56頁(yè)第57頁(yè)第58頁(yè)第59頁(yè)第60頁(yè)第61頁(yè)第62頁(yè)第63頁(yè)第64頁(yè)第65頁(yè)第66頁(yè)第67頁(yè)第68頁(yè)第69頁(yè)第70頁(yè)第71頁(yè)第72頁(yè)第73頁(yè)第74頁(yè)第75頁(yè)第76頁(yè)第77頁(yè)第78頁(yè)第79頁(yè)第80頁(yè)第81頁(yè)第82頁(yè)第83頁(yè)第84頁(yè)第85頁(yè)第86頁(yè)第87頁(yè)第88頁(yè)第89頁(yè)第90頁(yè)第91頁(yè)第92頁(yè)第93頁(yè)第94頁(yè)第95頁(yè)第96頁(yè)第97頁(yè)第98頁(yè)第99頁(yè)第100頁(yè)第101頁(yè)第102頁(yè)第103頁(yè)第104頁(yè)第105頁(yè)第106頁(yè)第107頁(yè)當(dāng)前第108頁(yè)第109頁(yè)第110頁(yè)第111頁(yè)第112頁(yè)第113頁(yè)第114頁(yè)第115頁(yè)第116頁(yè)第117頁(yè)第118頁(yè)第119頁(yè)第120頁(yè)第121頁(yè)第122頁(yè)第123頁(yè)第124頁(yè)第125頁(yè)第126頁(yè)第127頁(yè)第128頁(yè)第129頁(yè)第130頁(yè)第131頁(yè)第132頁(yè)第133頁(yè)第134頁(yè)第135頁(yè)第136頁(yè)第137頁(yè)第138頁(yè)第139頁(yè)第140頁(yè)第141頁(yè)第142頁(yè)第143頁(yè)第144頁(yè)第145頁(yè)第146頁(yè)第147頁(yè)第148頁(yè)第149頁(yè)第150頁(yè)
Rev.1.02
Nov 26, 2008
Page 58 of 146
REJ03B0224-0102
455A Group
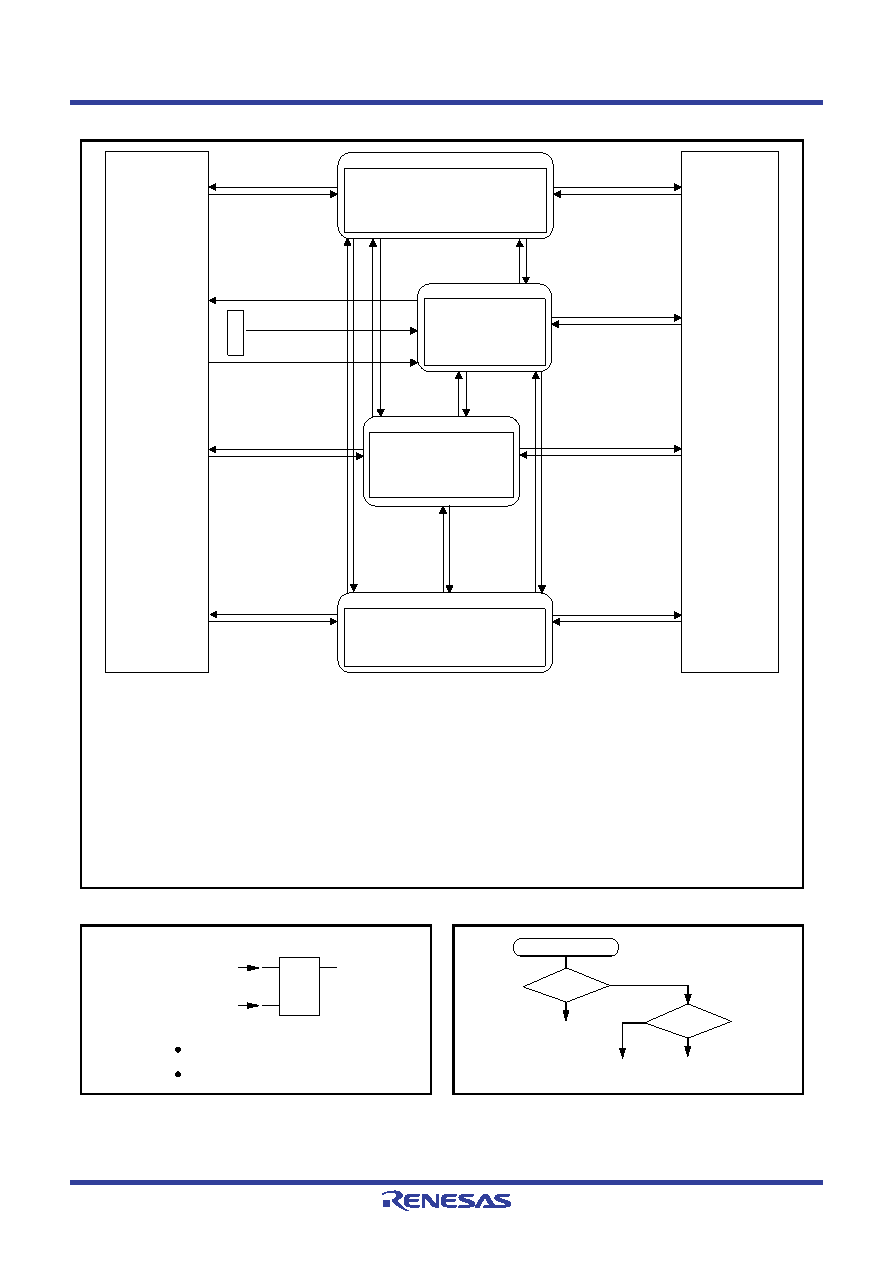
Fig 56. State transition
Fig 57. Set source and clear source of the P flag
Fig 58. Start condition identified example using the
SNZP instruction
Key-on wakeup
(Stabilizing time [d] )
F
RAM back-up
mode
f(HSOCO): stop
f(XIN): stop
f(XCIN): stop
f(LSOCO): stop
EPOF + POF2
instruction execution
Key-on wakeup
(Stabilizing time [c] )
B
Operation state
Operation source clock: f(XIN)
Ceramic resonator
D
Operation state
Operation source clock: f(LSOCO)
Low-spped on-chip oscillator
High-speed mode
EPOF + POF2
instruction execution
Key-on wakeup
(Stabilizing time [e] )
E
Clock operating mode
f(HSOCO): stop
f(XIN): stop
f(XCIN),
f(LSOCO):
by RG register
EPOF + POF
instruction execution
Key-on wakeup
Timer 3 underflow
(Stabilizing time [c] )
EPOF + POF
instruction execution
Key-on wakeup
Timer 3 underflow
(Stabilizing time [e] )
MR1, MR0
← 11
MR1, MR0
← 10
C
Operation state
Operation source clock: f(XCIN)
Quartz-crystal oscillation
EPOF + POF2
instruction execution
EPOF + POF
instruction execution
Key-on wakeup
Timer 3 underflow
(Stabilizing time [d] )
MR1, MR0
← 10
MR1, MR0
← 00
A
Operation state
Operation source clock:
f(HSOCO)
High-speed on-chip oscillator
EPOF + POF2
instruction execution
Key-on wakeup
(Stabilizing time [b] )
EPOF + POF
instruction execution
Key-on wakeup
Timer 3 underflow
(Stabilizing time [b] )
(Stabilizing time [a] )
MR1, MR0
← 00
MR1, MR0
← 01
MR
1
,MR
0
←
11
MR
1
,MR
0
←
01
MR
1
,M
R
0
←
11
MR
1
,MR0
←
00
Internal mode
Low-speed mode
M
R
1,
M
R
0
←
10
MR
1
,MR
0
←
01
Internal low-speed mode
Res
e
t
1. The system clock selected by the clock control registers MR and RG is retained at power down.
The oscillation stability time at return can be adjusted by setting the clock control registers MR and RG before transiting to
the power down state.
2. To transmit to the clock operating mode, the EPOF and POF instructions must be executed continuously.
3. To transmit to the RAM back-up mode, the EPOF and POF2 instructions must be executed continuously.
4. After reset release, the main clock (f(XIN)), the sub-clock, and the internal clock (f(HSOCO)) are enabled.
5. To select a stopped clock as the system clock, first start the clock selected by the clock control register RG and generate
the oscillation stability time by software. Then switch the system clock.
Stabilizing time [a] : Microcomputer starts its operation after counting the f(HSOCO) to 1376 times.
Stabilizing time [b] : Microcomputer starts its operation after counting the f(HSOCO) to (system clock division ratio X 15) times.
Stabilizing time [c] : Microcomputer starts its operation after counting the f(XIN) to (system clock division ratio X 171) times.
Stabilizing time [d] : Microcomputer starts its operation after counting the f(XCIN) to (system clock division ratio X 171) times.
Stabilizing time [e] : Microcomputer starts its operation after counting the f(LSOCO) to (system clock division ratio X 15) times.
Notes
S
R
Q
Power downflagP
POF or
POF2
instruction
Reset input
Set source
Clear source
System reset
EPOF instruction +
POF or
POF2
instruction
EPOF instruction +
P
Program start
P= “1”
?
Warm start
Cold start
No
T3F =
?
Return from
timer 3 underflow
Return from
external wakeup signal
“1”
Yes
No
SNZT3
instruction
SNZP
instruction
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| M3455AGC-XXXFP | 4-BIT, OTPROM, 6 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP52 |
| M3455AG8-XXXFP | 4-BIT, OTPROM, 6 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP52 |
| M34570MD-XXXFP | 4-BIT, MROM, 2 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PDSO36 |
| M34570E8FP | 4-BIT, OTPROM, 2 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PDSO36 |
| M34583EDFP | 4-BIT, OTPROM, 6 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP32 |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| M3455AG8-XXXFP | 制造商:RENESAS 制造商全稱:Renesas Technology Corp 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 4-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M3455AGCFP | 制造商:RENESAS 制造商全稱:Renesas Technology Corp 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 4-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M3455AGC-XXXFP | 制造商:RENESAS 制造商全稱:Renesas Technology Corp 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 4-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M3455-SL001 | 制造商:Alpha Wire 功能描述: |
| M3455-SL002 | 制造商:Alpha Wire 功能描述: |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。