- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄383714 > OR2T04A-4BC208 (Electronic Theatre Controls, Inc.) Field-Programmable Gate Arrays PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | OR2T04A-4BC208 |
| 廠商: | Electronic Theatre Controls, Inc. |
| 元件分類: | FPGA |
| 英文描述: | Field-Programmable Gate Arrays |
| 中文描述: | 現(xiàn)場可編程門陣列 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 8/192頁 |
| 文件大小: | 3148K |
| 代理商: | OR2T04A-4BC208 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁當前第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁第103頁第104頁第105頁第106頁第107頁第108頁第109頁第110頁第111頁第112頁第113頁第114頁第115頁第116頁第117頁第118頁第119頁第120頁第121頁第122頁第123頁第124頁第125頁第126頁第127頁第128頁第129頁第130頁第131頁第132頁第133頁第134頁第135頁第136頁第137頁第138頁第139頁第140頁第141頁第142頁第143頁第144頁第145頁第146頁第147頁第148頁第149頁第150頁第151頁第152頁第153頁第154頁第155頁第156頁第157頁第158頁第159頁第160頁第161頁第162頁第163頁第164頁第165頁第166頁第167頁第168頁第169頁第170頁第171頁第172頁第173頁第174頁第175頁第176頁第177頁第178頁第179頁第180頁第181頁第182頁第183頁第184頁第185頁第186頁第187頁第188頁第189頁第190頁第191頁第192頁
8
Lucent Technologies Inc.
Data Sheet
June 1999
ORCA Series 2 FPGAs
Programmable Logic Cells
(continued)
The LUT ripple mode operation offers standard arith-
metic functions, such as 4-bit adders, subtractors,
adder/subtractors, and counters. In the ORCA
Series 2, there are two new ripple modes available.
The first new mode is a 4 x 1 multiplier, and the second
is a 4-bit comparator. These new modes offer the
advantages of faster speeds as well as denser logic
capabilities.
When the LUT is configured to operate in the memory
mode, a 16 x 2 asynchronous memory fits into an
HLUT. Both the MA and MB modes were available in
previous ORCA architectures, and each mode can be
configured in an HLUT separately. In the Series 2,
there are two new memory modes available. The first is
a 16 x 4 synchronous single-port memory (SSPM), and
the second is a 16 x 2 synchronous dual-port memory
(SDPM). These new modes offer easier implementa-
tion, faster speeds, denser RAMs, and a dual-port
capability that wasn’t previously offered as an option in
the ATT2Cxx/ATT2Txx families.
If the LUT is configured to operate in the ripple mode, it
cannot be used for basic combinatorial logic or memory
functions. In modes other than the ripple, SSPM, and
SDPM modes, combinations of operating modes are
possible. For example, the LUT can be configured as a
16 x 2 RAM in one HLUT and a five-input combinatorial
logic function in the second HLUT. This can be done by
configuring HLUTA in the MA mode and HLUTB in the
F5B mode (or vice versa).
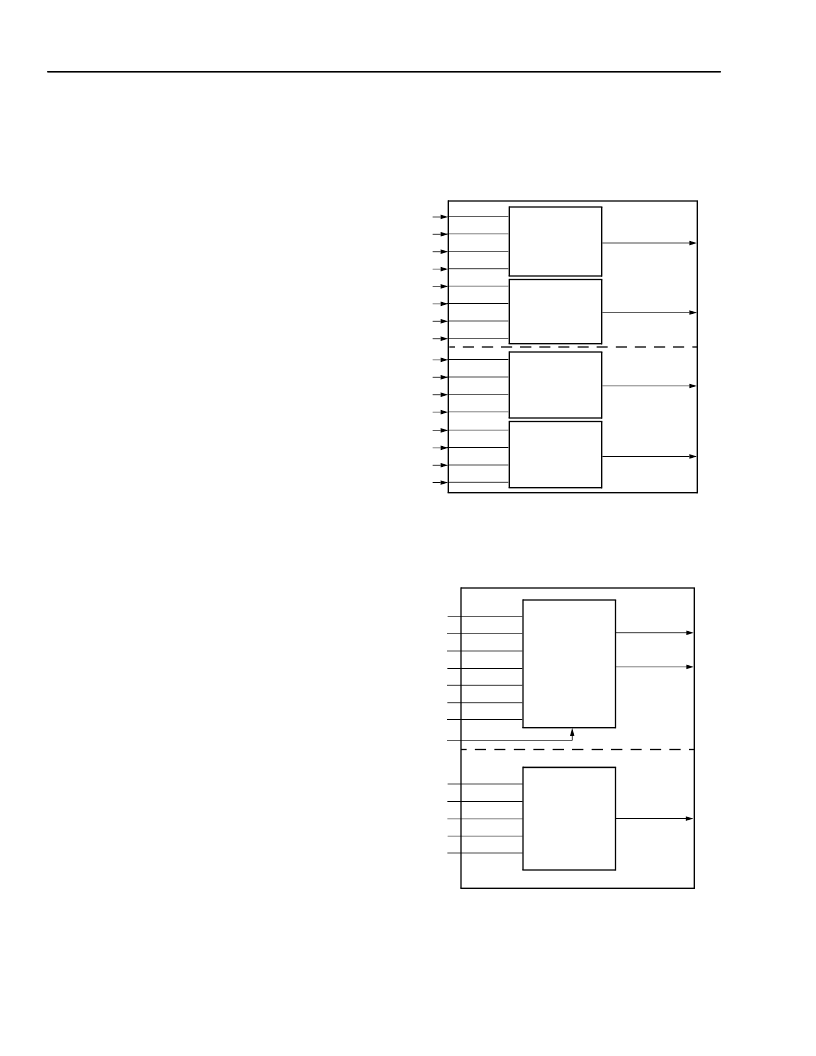
F4A/F4B Mode—Two Four-Input Functions
Each HLUT can be used to implement two four-input
combinatorial functions, but the total number of inputs
into each HLUT cannot exceed five. The two QLUTs
within each HLUT share three inputs. In HLUTA, the
A1, A2, and A3 inputs are shared by QLUT2 and
QLUT3. Similarly, in HLUTB, the B1, B2, and B3 inputs
are shared by QLUT0 and QLUT1. The four outputs
are F0, F1, F2, and F3. The results can be routed to
the D0, D1, D2, and D3 latch/FF inputs or as an output
of the PFU. The use of the LUT for four functions of up
to four inputs each is given in Figure 4.
F5A/F5B Mode—One Five-Input Variable Function
Each HLUT can be used to implement any five-input
combinatorial function. The input ports are A[4:0] and
B[4:0], and the output ports are F0 and F3. One five or
less input function is input into A[4:0], and the second
five or less input function is input into B[4:0]. The
results are routed to the latch/FF D0 and latch/FF D3
inputs, or as a PFU output. The use of the LUT for two
independent functions of up to five inputs is shown in
Figure 5. In this case, the LUT is configured in the F5A
and F5B modes. As a variation, the LUT can do one
function of up to five input variables and two four-input
functions using F5A and F4B modes or F4A and F5B
modes.
5-2753(F).r2
Figure 4. F4 Mode—Four Functions of Four-
Input Variables
5-2845(F).r2
Figure 5. F5 Mode—Two Functions of Five-Input
Variables
QLUT2
A3
A3
A2
A1
A0
A2
A1
A0
F2
QLUT3
A4
A4
A3
A2
A1
A3
A2
A1
F3
HLUTA
QLUT0
B3
B3
B2
B1
B0
B2
B1
B0
F0
QLUT1
B4
B4
B3
B2
B1
B3
B2
B1
F1
HLUTB
QLUT3
QLUT2
F3
QLUT1
QLUT0
B4
B3
B2
B1
B0
F0
WEA
A3
A2
A1
A0
B4
B3
B2
B1
B0
A4
A3
A2
A1
A0
WD3
HLUTA
HLUTB
c0
WPE
WD3
WD2
WD2
F2
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| OR2T04A-4BC208I | Field-Programmable Gate Arrays |
| OR2T04A-4BC84 | Field-Programmable Gate Arrays |
| OR2T04A-4M160I | Field-Programmable Gate Arrays |
| OR2T04A-4M208 | Field-Programmable Gate Arrays |
| OR2T04A-4M208I | Field-Programmable Gate Arrays |
相關代理商/技術參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| OR2T04A-4BC208I | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Field-Programmable Gate Arrays |
| OR2T04A-4BC84 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Field-Programmable Gate Arrays |
| OR2T04A-4BC84I | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Field-Programmable Gate Arrays |
| OR2T04A-4J100 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Field-Programmable Gate Arrays |
| OR2T04A-4J100I | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Field-Programmable Gate Arrays |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。