- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄383646 > MT9173AP (Mitel Networks Corporation) Digital Subscriber Interface Circuit with RxSB PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | MT9173AP |
| 廠商: | Mitel Networks Corporation |
| 英文描述: | Digital Subscriber Interface Circuit with RxSB |
| 中文描述: | 數(shù)字用戶接口電路RxSB |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 12/22頁 |
| 文件大小: | 411K |
| 代理商: | MT9173AP |
MT9173/74
Preliminary Information
9-148
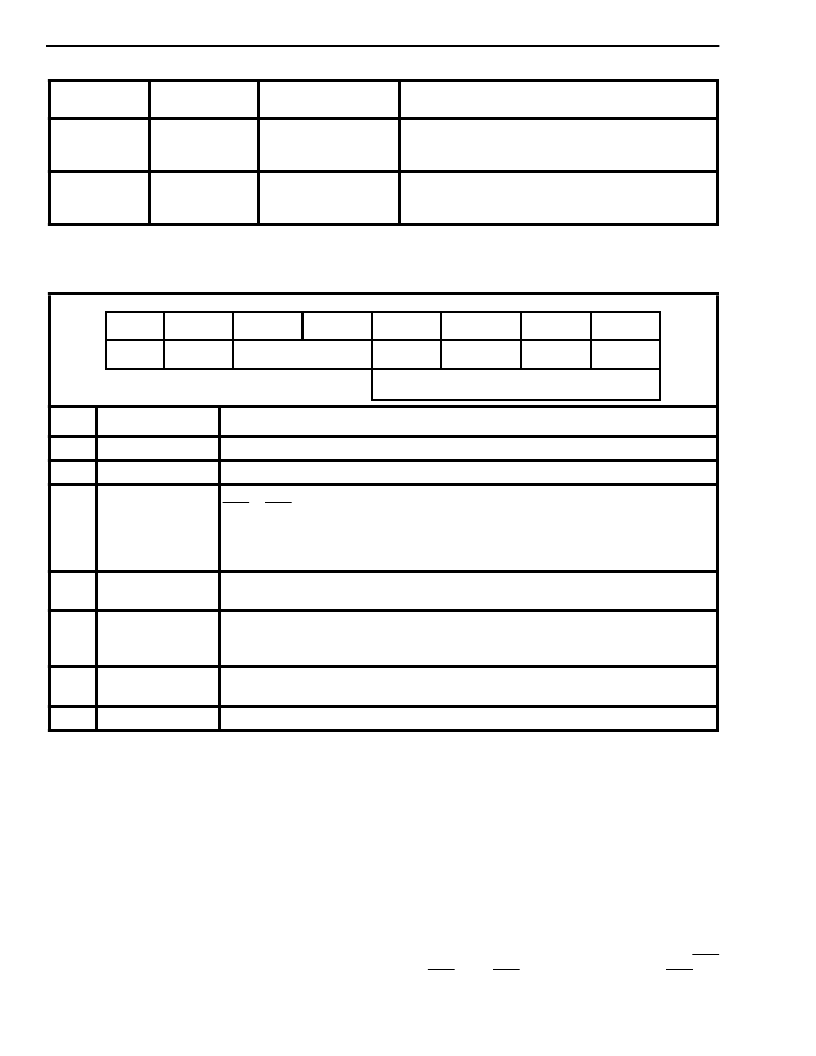
Table 4a. Default Mode Selection
Notes:
Default Mode 1 can also be selected by tying CDSTi/CDi pin low when DNIC is operating in dual mode.
Default Mode 2 can also be selected by tying CDSTi/CDi pin high when DNIC is operating in dual mode.
Table 5. Diagnostic Register
Notes:
depending upon the status of bit-3.
Do not use L
OUT
to L
IN
loopback in DN/SLV mode.
Do not use DSTo to DSTi loopback in MOD/MAS mode.
When bits 4-7 of the Diagnostic Register are all set to one, the DNIC operates in one of the default modes as defined in Table 4a,
C-Channel
(Bit 0-7)
Internal Control
Register
Internal Diagnostic
Register
Description
XXX01111
00000000
01000000
Default Mode-1
: Bit rate is 80 kbit/s. ATTACK,
PSEN, DINB, DRR and all diagnostics are disabled.
TxHK=0.
Default Mode-2
Bit rate is 160 kbit/s. ATTACK,
PSEN, DINB, DRR and all diagnostics are disabled.
TxHK=0.
XXX11111
00010000
01000000
Bit
Name
Description
0
Reg Sel-1
Register Select-1. Must be set to ’0’ to select the Diagnostic Register.
1
Reg Sel-2
Register Select-2. Must be set to ’1’ to select the Diagnostic Register.
2,3
Loopback
Bit 2
0
0
1
1
Bit 3
0
1
0
1
All loopback testing functions disabled. Normal operation.
DSTi internally looped back into DSTo for system diagnostics.
L
OUT
is internally looped back into L
IN
for system diagnostics.
DSTo is internally looped back into DSTi for end-to-end testing.
4
FUN
Force Unsync. When set to ’1’, the DNIC is forced out-of-sync to test the SYNC
recovery circuitry. When set to ’0’, the operation continues in synchronization.
5
PSWAP
Polynomial Swap. When set to ’1’, the scrambling and descrambling polynomials
are interchanged (use for MAS mode only). When set to ’0’, the polynomials retain
their normal designations.
6
DLO
Disable Line Out. When set to ’1’, the signal on L
OUT
is set set to V
Bias
. When set to
’0’, L
OUT
pin functions normally.
Must be set to ’0’ for normal operation.
7
Not Used
bit 0
bit 1
bit 2
bit 3
bit 4
bit 5
bit 6
bit 7
Reg Sel-1
Reg Sel-2
Loopback
FUN
PSWAP
DLO
Not Used
Default Mode Selection
(Refer to Table 4a)
The Diagnostics Register Reset bit (bit 2) of the
Control Register determines the reset state of the
Diagnostics Register. If, on writing to the Control
Register, this bit is set to logic “0”, the Diagnostics
Register will be reset coincident with the frame
pulse. When this bit is logic “1”, the Diagnostics
Register will not be reset. In order to use the
diagnostic features, the Diagnostics Register must
be continuously written to. The output C-channel
sends status information from the Status Register to
the system along with the received HK bit as shown
in Table 6.
In MOD mode, the CD port is no longer an ST-BUS
but is a serial bit stream operating at the bit rate
selected. It continues to transfer the C-channel but
the D-channel and the HK bit no longer exist. DUAL
port operation must be used in MOD mode. The C-
channel is clocked in and out of the CD port by TCK
and CLD with TCK defining the bits and CLD the
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MT9173 | Digital Subscriber Interface Circuit with RxSB |
| MT9173 | Digital Subscriber Interface Circuit with RxSB(數(shù)字用戶接口電路(帶接收同步位)) |
| MT9174 | Digital Network Interface Circuit with RxSB(數(shù)字網(wǎng)絡接口電路(帶接收同步位)) |
| MT9196 | Integrated Digital Phone Circuit (IDPC)(集成數(shù)字電話電路) |
| MT91L60 | 3 Volt Multi-Featured Codec (MFC)(3V 多特性編解碼器) |
相關代理商/技術參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| MT9173AP1 | 制造商:Microsemi Corporation 功能描述:DGTL INTRFC CIRCUIT 28PLCC - Rail/Tube |
| MT9174 | 制造商:MITEL 制造商全稱:Mitel Networks Corporation 功能描述:ISO2-CMOS ST-BUS⑩ FAMILY Digital Network Interface Circuit with Receive Sync Marker Bit |
| MT9174AE | 制造商:ZARLINK 制造商全稱:Zarlink Semiconductor Inc 功能描述:Digital Subscriber Interface Circuit with RxSB Digital Network Interface Circuit with RxSB |
| MT9174AN | 制造商:Microsemi Corporation 功能描述:DGTL INTRFC CIRCUIT 24SSOP - Rail/Tube |
| MT9174AN1 | 制造商:Microsemi Corporation 功能描述:DGTL INTRFC CIRCUIT 24SSOP - Rail/Tube 制造商:MICROSEMI CONSUMER MEDICAL PRODUCT GROUP 功能描述:IC SUBSCRIBER NETWRK DNIC 24SSOP 制造商:Microsemi Corporation 功能描述:IC SUBSCRIBER NETWRK DNIC 24SSOP |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。