- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄383643 > MT8940 (Mitel Networks Corporation) ISO-CMOS ST-BUS⑩ FAMILY T1/CEPT Digital Trunk PLL PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | MT8940 |
| 廠商: | Mitel Networks Corporation |
| 英文描述: | ISO-CMOS ST-BUS⑩ FAMILY T1/CEPT Digital Trunk PLL |
| 中文描述: | 異意法半導(dǎo)體的CMOS總線⑩家庭T1/CEPT數(shù)字集群鎖相環(huán) |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 7/16頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 299K |
| 代理商: | MT8940 |
ISO-CMOS
MT8940
3-33
Applications
The following figures illustrate how the MT8940 can
be used in a minimum component count approach to
providing the timing and synchronization signals for
the Mitel T1 and CEPT interfaces, and the ST-BUS.
The
hardware
selectable
independent control over each PLL adds flexibility to
the interface circuits. It can be easily reconfigured to
provide the timing and control signals for both at the
master and slave ends of the link.
modes
and
the
Synchronization and Timing Signals for the T1
Transmission Link
Figures 4 and 5 show examples of how to generate
the timing signals for the master and slave ends of a
T1 link.
At the master end of the link (Figure 4), DPLL #2 is
the source of the ST-BUS signals derived from the
4.096 MHz system clock. The frame pulse output is
looped back to DPLL #1 (in NORMAL mode), which
locks to it to generate the T1 line clock. The timing
relationship between the 1.544 MHz T1 clock and the
2.048 MHz ST-BUS clock meets the requirements of
the MH89760/760B. The crystal clock at 12.355 MHz
is used by DPLL #1 to generate the 1.544 MHz clock,
while DPLL #2 uses the 4.096 MHz system clock to
provide the ST-BUS timing signals. The ST-BUS
signals can also be obtained from DPLL #2 in FREE-
RUN mode, using a crystal clock at 16.388 MHz
instead
of
4.096
MHz
system
clock.
The
uncommitted NAND gate converts the received
signals, RxA and RxB of the MH89760 to a single
Return to Zero (RZ) input for the clock extraction
circuits of the MH89760. This is not required for the
MH89760B. The generated ST-BUS signals can be
used to synchronize the system and the switching
equipment at the master end.
At the slave end of the link (Figure 5) both the DPLLs
are in NORMAL mode with DPLL #2 providing the
ST-BUS timing signals locked to the 8 kHz frame
pulse (E8Ko) extracted from the received signal on
the T1 line. The regenerated frame pulse is looped
back to DPLL #1 to provide the T1 line clock as at
the master end. The 12.355 MHz and 16.388 MHz
crystal clock sources are necessary for DPLL #1 and
#2.
Synchronization and Timing Signals for the
CEPT Transmission Link
The MT8940 can be used to provide the timing and
synchronization signals for the MH89790/790B,
MITEL’s CEPT(30+2) digital trunk interface hybrid.
Since the operational frequencies of the ST-BUS and
the CEPT primary multiplex digital trunk are same,
only DPLL #2 is required to achieve synchronization
between the two
.
Figures 6 and 7 show how the MT8940 can be used
to synchronize the ST-BUS and the CEPT
transmission link at the master and slave ends,
respectively.
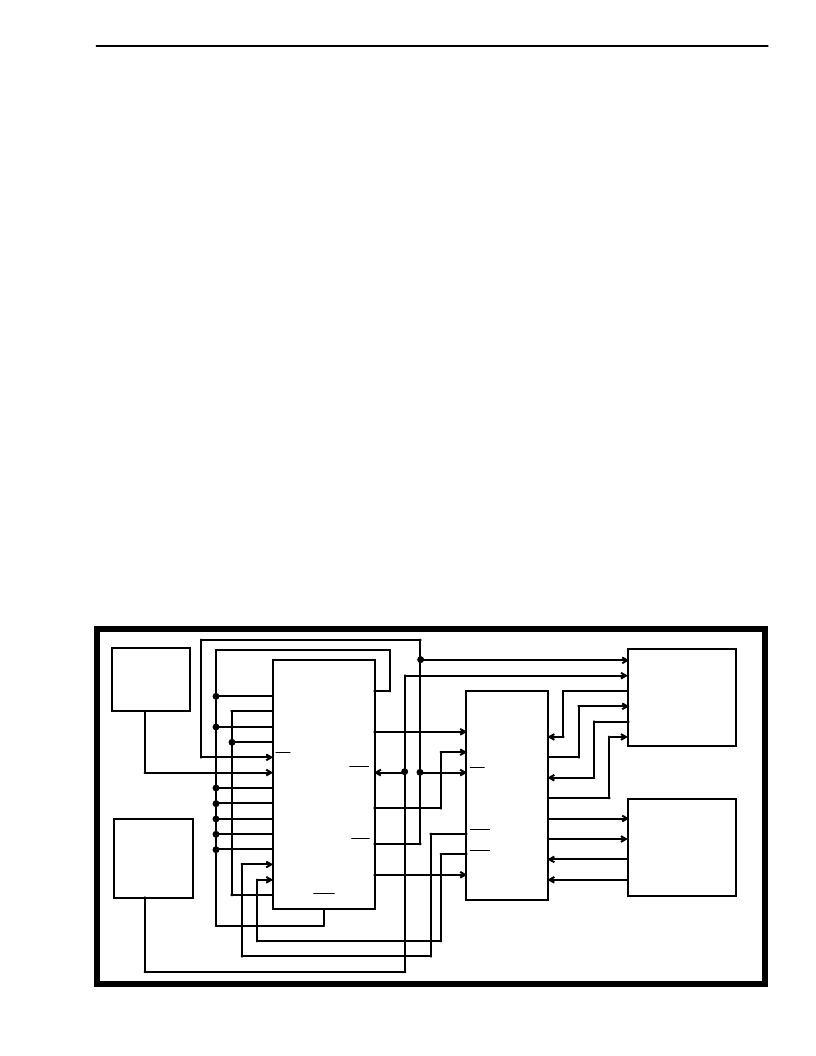
Figure 4 - Synchronization at the Master End of the T1 Transmission Link
Crystal Clock
(12.355 MHz
±
100 ppm)
4.096 MHz
System Clock
(ST-BUS
compatible)
MT8940
MS0
MS1
MS2
MS3
F0i
C12i
EN
CV
C8Kb
C16i
EN
C4o
EN
C2o
Ai
Bi
V
SS
V
DD
CV
C4b
C2o
F0b
Y
o
RST
MH89760
C1.5i
C2i
F0i
RxA
RxB
RxD
DSTi
DSTo
CSTi
CSTo
TxT
TxR
RxT
RxR
MT8980/81
ST-BUS
SWITCH
T1
LINK
(1.544 Mbps)
TRANSMIT
RECEIVE
MODE OF OPERATION FOR THE MT8940
DPLL #1 - NORMAL (MS0 = X; MS1 = 0)
DPLL #2 - OVERRIDE THE MAJOR MODES (MS2 = 1; MS3 = 0)
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MT8940-1 | ISO-CMOS ST-BUS⑩ FAMILY T1/CEPT Digital Trunk PLL |
| MT8940AC | T1/CEPT Digital Trunk PLL |
| MT8940AE | ISO-CMOS ST-BUS⑩ FAMILY T1/CEPT Digital Trunk PLL |
| MT8941B | Advanced T1/CEPT Digital Trunk PLL(先進(jìn)的T1/CEPT數(shù)字中繼鎖相環(huán)) |
| MT8941B | CMOS ST-BUS⑩ FAMILY Advanced T1/CEPT Digital Trunk PLL |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| MT8940-1 | 制造商:MITEL 制造商全稱:Mitel Networks Corporation 功能描述:ISO-CMOS ST-BUS⑩ FAMILY T1/CEPT Digital Trunk PLL |
| MT8940AC | 制造商:MITEL 制造商全稱:Mitel Networks Corporation 功能描述:T1/CEPT Digital Trunk PLL |
| MT8940AE | 制造商:MITEL 功能描述: |
| MT8941 | 制造商:ZARLINK 制造商全稱:Zarlink Semiconductor Inc 功能描述:Advanced T1/CEPT Digital Trunk PLL |
| MT8941AE | 制造商:MITEL 制造商全稱:Mitel Networks Corporation 功能描述:CMOS ST-BUS⑩ FAMILY Advanced T1/CEPT Digital Trunk PLL |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。