- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄43901 > L6919E (STMICROELECTRONICS) SWITCHING CONTROLLER, PDSO28 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | L6919E |
| 廠商: | STMICROELECTRONICS |
| 元件分類: | 穩(wěn)壓器 |
| 英文描述: | SWITCHING CONTROLLER, PDSO28 |
| 封裝: | SO-28 |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 2/33頁(yè) |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 644K |
| 代理商: | L6919E |
第1頁(yè)當(dāng)前第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)第21頁(yè)第22頁(yè)第23頁(yè)第24頁(yè)第25頁(yè)第26頁(yè)第27頁(yè)第28頁(yè)第29頁(yè)第30頁(yè)第31頁(yè)第32頁(yè)第33頁(yè)
Obsolete
Product(s)
- Obsolete
Product(s)
L6919E
10/33
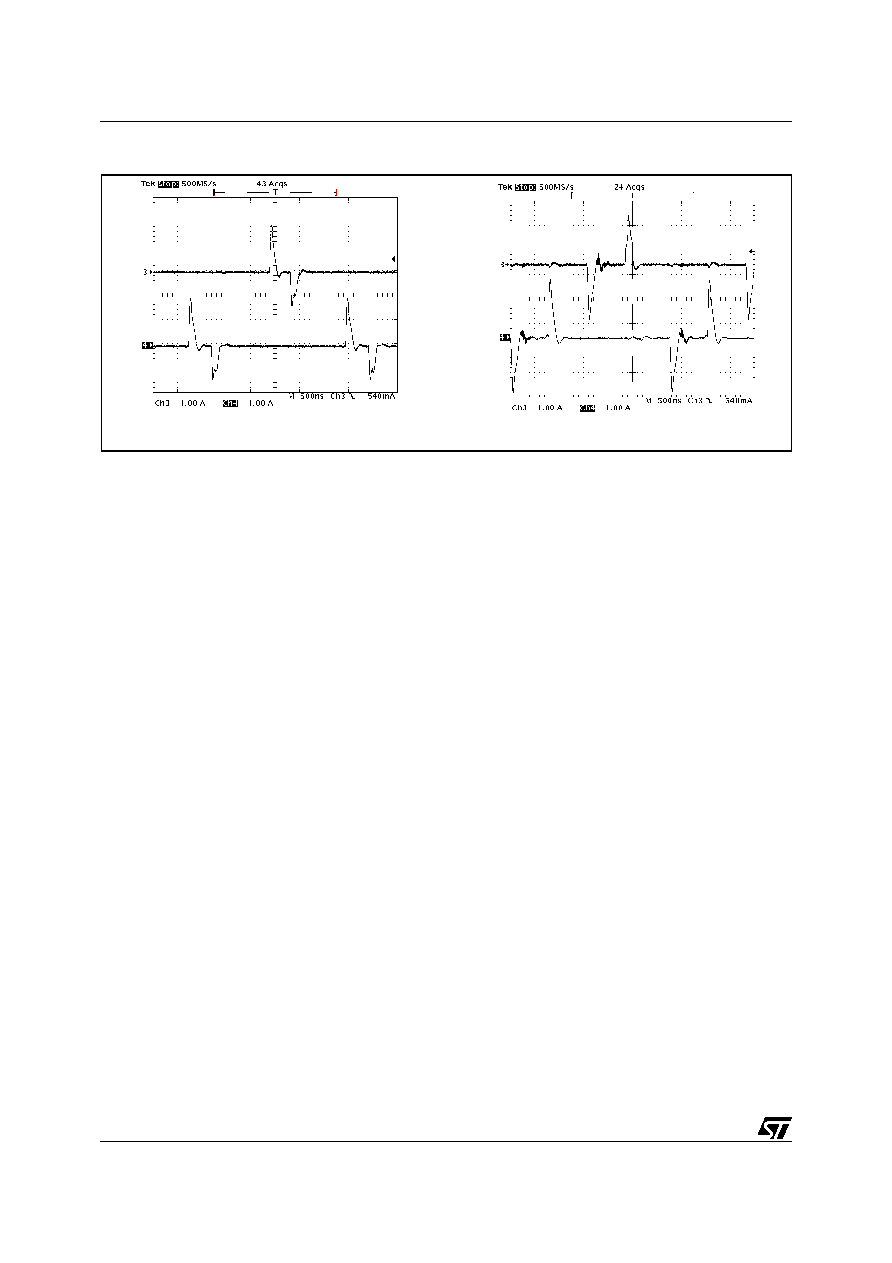
Figure 3. Drivers peak current: High Side (left) and Low Side (right)
To allow the turning on of the low-side mosfet even in this case, a watchdog controller is enabled: if the source
of the high-side mosfet don't drop for more than 240ns, the low side mosfet is switched on so allowing the neg-
ative current of the inductor to recirculate. This mechanism allows the system to regulate even if the current is
negative.
The BOOTx and VCCDR pins are separated from IC's power supply (VCC pin) as well as signal ground (SGND
pin) and power ground (PGND pin) in order to maximize the switching noise immunity. The separated supply
for the different drivers gives high flexibility in mosfet choice, allowing the use of logic-level mosfet. Several com-
bination of supply can be chosen to optimize performance and efficiency of the application. Power conversion
is also flexible; 5V or 12V bus can be chosen freely.
The peak current is shown for both the upper and the lower driver of the two phases in figure 3. A 10nF capac-
itive load has been used. For the upper drivers, the source current is 1.9A while the sink current is 1.5A with
VBOOT -VPHASE = 12V; similarly, for the lower drivers, the source current is 2.4A while the sink current is 2A with
VCCDR = 12V.
CURRENT READING AND OVER CURRENT
The current flowing trough each phase is read using the voltage drop across the low side mosfets RdsON or
across a sense resistor (RSENSE) and internally converted into a current. The Tran conductance ratio is issued
by the external resistor Rg placed outside the chip between ISENx and PGNDSx pins toward the reading points.
The full differential current reading rejects noise and allows to place sensing element in different locations with-
out affecting the measurement's accuracy. The current reading circuitry reads the current during the time in
which the low-side mosfet is on (OFF Time). During this time, the reaction keeps the pin ISENx and PGNDSx
at the same voltage while during the time in which the reading circuitry is off, an internal clamp keeps these two
pins at the same voltage sinking from the ISENx pin the necessary current (Needed if low-side mosfet RdsON
sense is implemented to avoid absolute maximum rating overcome on ISENx pin).
The proprietary current reading circuit allows a very precise and high bandwidth reading for both positive and
negative current. This circuit reproduces the current flowing through the sensing element using a high speed
Track & Hold Tran conductance amplifier. In particular, it reads the current during the second half of the OFF
time reducing noise injection into the device due to the mosfet turn-on (See fig. 4). Track time must be at least
200ns to make proper reading of the delivered current
This circuit sources a constant 50
A current from the PGNDSx pin and keeps the pins ISENx and PGNDSx at
the same voltage. Referring to figure 4, the current that flows in the ISENx pin is then given by the following
equation:
CH3 = HGATE1; CH4 = HGATE2
CH3 = LGATE1; CH4 = LGATE2
I
ISENx
50
A
R
SENSE
I
PHASE
R
g
----------------------------------------------
+
50
AI
IN FO x
+
==
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| L6920DTR | 1.2 A SWITCHING REGULATOR, PDSO8 |
| L6920D | 1.2 A SWITCHING REGULATOR, PDSO8 |
| L6920 | 1.2 A SWITCHING REGULATOR, PDSO8 |
| L6924D013TR | 1-CHANNEL POWER SUPPLY SUPPORT CKT, QCC16 |
| L6926D | 1.4 A SWITCHING REGULATOR, 600 kHz SWITCHING FREQ-MAX, PDSO8 |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| L6919ETR | 功能描述:DC/DC 開關(guān)控制器 5-Bit Dual Ph Contlr RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 輸入電壓:6 V to 100 V 開關(guān)頻率: 輸出電壓:1.215 V to 80 V 輸出電流:3.5 A 輸出端數(shù)量:1 最大工作溫度:+ 125 C 安裝風(fēng)格: 封裝 / 箱體:CPAK |
| L-692 | 制造商:RHOMBUS-IND 制造商全稱:Rhombus Industries Inc. 功能描述:Common Mode Inductor |
| L6920 | 制造商:STMICROELECTRONICS 制造商全稱:STMicroelectronics 功能描述:1V HIGH EFFICIENCY SYNCRONOUS STEP UP CONVERTER |
| L6920D | 功能描述:直流/直流開關(guān)轉(zhuǎn)換器 0.6 to 5.5V Step-Up RoHS:否 制造商:STMicroelectronics 最大輸入電壓:4.5 V 開關(guān)頻率:1.5 MHz 輸出電壓:4.6 V 輸出電流:250 mA 輸出端數(shù)量:2 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT |
| L6920DB | 功能描述:直流/直流開關(guān)轉(zhuǎn)換器 Synchronous Rectifer Step Up Converter RoHS:否 制造商:STMicroelectronics 最大輸入電壓:4.5 V 開關(guān)頻率:1.5 MHz 輸出電壓:4.6 V 輸出電流:250 mA 輸出端數(shù)量:2 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。