- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄196437 > TK11231CUCB (TOKO INC) 3.1 V FIXED POSITIVE LDO REGULATOR, 0.37 V DROPOUT, PDSO6 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | TK11231CUCB |
| 廠商: | TOKO INC |
| 元件分類: | 固定正電壓單路輸出LDO穩(wěn)壓器 |
| 英文描述: | 3.1 V FIXED POSITIVE LDO REGULATOR, 0.37 V DROPOUT, PDSO6 |
| 封裝: | SOT-89, 6-PIN |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 8/22頁 |
| 文件大小: | 542K |
| 代理商: | TK11231CUCB |
TOKO Inc.
IC Data Sheet
TK112xxC
GC3-H026
GC3-H026B
B
BPage
Page
Page 16
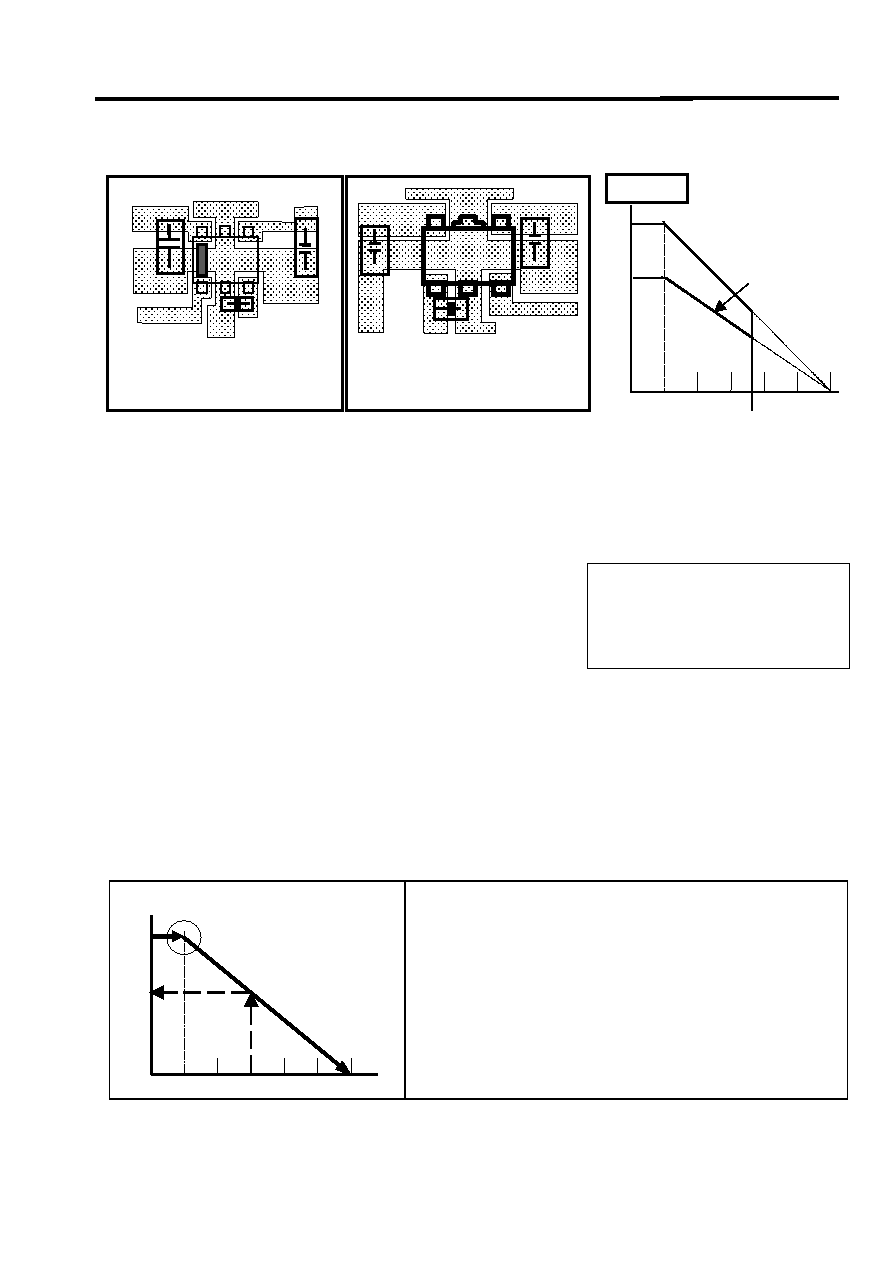
Layout
Layout PCB Material : Glass epoxy t=0.8mm
SOT23L-6
SOT89-5
Derating Curve
The package loss is limited at the temperature that the internal temperature sensor works (about 150
°C).
Therefore, the package loss is assumed to be an internal limitation. There is no heat radiation
characteristic of the package unit assumed because of the small size. Heat is carried away by the device
being installed on the PCB. This value changes by the material and the copper pattern etc. of the PCB.
The losses are approximately 600mW (SOT-23L) : 900mW(SOT-89). Enduring these losses becomes
possible in a lot of applications operating at 25
°C.
Determining the thermal resistance when mounted on
Determining the thermal resistance when mounted on aaaa PCB.
PCB.
The operating chip junction temperature is shown by
Tj=
θja × Pd + Ta.
Tj of the IC is set to about 150
°C.
Pd is a value when the overtemperature sensor is made to work.
Pd is
Pd is easily
easily
easily obtained.
obtained.
Mount the IC on the print circuit board. Short between the output pin and ground. after that, raise input
voltage from 0V to evaluated voltage (see*1) gradually.
At shorted the output pin, the power dissipation PD can be expressed as Pd=Vin × Iin.
The input current decreases gradually as the temperature of the chip becomes high. After a while, it
reaches the thermal equilibrium. Use this currrent value at the thermal equilibrium. In almost all the
cases, it shows 600mW(SOT23L-6) 900mW(SOT89-5) or more.
*1 In the case that the power, Vin
× Ishort(Short Circuit Current), becomes more than twice of the maximum rating of its power
dissipation in a moment, there is a possibility that the IC is destroyed before internal thermal protection works.
Pd is obtained by the normal temperature in degrees. The current that can be used at the highest
operating temperature is obtained from the graph of the figure below.
Procedure (Do when PCB mounted).
1. Pd is obtained (Vin
× Iin when the output side is short-circuited).
2. Pd is plotted on the horizontal line to 25
°C.
3. Pd is connected with the point of 150
°C by the straight line
(bold face line).
4. A line is extended vertically above the point of use temperature in the
design. For instance, 75
°C is assumed (broken line).
5. Extend the intersection of the derating curve (fat solid line) and (broken
line) to the left and read the Pd value.
6. DPd
÷÷÷÷ (Vinmax Vout)=Iout (at 75°C)
The maximum current that can be used at the highest operating temperature is:
Iout
DPd
DPd
÷÷÷÷ ((((Vinmax
Vinmax
Vout).
Vout).
Please do derating with 4mW/
°C at
Pd=600mW and 25
°C or more. Thermal
resistance is (
θja=250°C / W).
Vout
On/off
Vin
Please do derating with 7.2mW/
°C at
Pd=900mW
and
25
°C or more.
Thermal resistance is (
θja=138°C / W)
600
SOT-89
-7.2mW/
°C
25
50
°C
100
150
0
Pd(mW)
(85)
°C
900
SOT-23- L
-4.8mW/
°C
0
on/off
Vin
Vout
Ta (Ta=25
°C)
150 =
θja × pd + 25
θja × Pd = 125
θja = (125/ pd) (°C / mW)
Pd(mW)
25 50
100
150
°C
0
(75)
DPd
Pd
2
3
4
5
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| TK11243CUIB | 4.3 V FIXED POSITIVE LDO REGULATOR, 0.37 V DROPOUT, PDSO6 |
| TK11243CUCB | 4.3 V FIXED POSITIVE LDO REGULATOR, 0.37 V DROPOUT, PDSO6 |
| TK11249CUIB | 4.9 V FIXED POSITIVE LDO REGULATOR, 0.37 V DROPOUT, PDSO6 |
| TK11249CUCB | 4.9 V FIXED POSITIVE LDO REGULATOR, 0.37 V DROPOUT, PDSO6 |
| TK11219CMIL | 1.9 V FIXED POSITIVE LDO REGULATOR, 0.37 V DROPOUT, PDSO6 |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| TK11232B | 制造商:TOKO 制造商全稱:TOKO, Inc 功能描述:VOLTAGE REGULATOR WITH ON/OFF SWITCH |
| TK11232BMCB | 制造商:TOKO 制造商全稱:TOKO, Inc 功能描述:VOLTAGE REGULATOR WITH ON/OFF SWITCH |
| TK11232BMCL | 制造商:TOKO 制造商全稱:TOKO, Inc 功能描述:VOLTAGE REGULATOR WITH ON/OFF SWITCH |
| TK11232BMIB | 制造商:TOKO 制造商全稱:TOKO, Inc 功能描述:VOLTAGE REGULATOR WITH ON/OFF SWITCH |
| TK11232BMIL | 制造商:TOKO 制造商全稱:TOKO, Inc 功能描述:VOLTAGE REGULATOR WITH ON/OFF SWITCH |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。