- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄98229 > THS7374IPW (TEXAS INSTRUMENTS INC) 4 CHANNEL, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO14 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | THS7374IPW |
| 廠商: | TEXAS INSTRUMENTS INC |
| 元件分類: | 音頻/視頻放大 |
| 英文描述: | 4 CHANNEL, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO14 |
| 封裝: | GREEN, PLASTIC, TSSOP-14 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 14/40頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 929K |
| 代理商: | THS7374IPW |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁當(dāng)前第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁
Level
Shift
Internal
Circuitry
+V
S
800kW
Input
Pin
www.ti.com
SLOS590B – JULY 2008 – REVISED JANUARY 2011
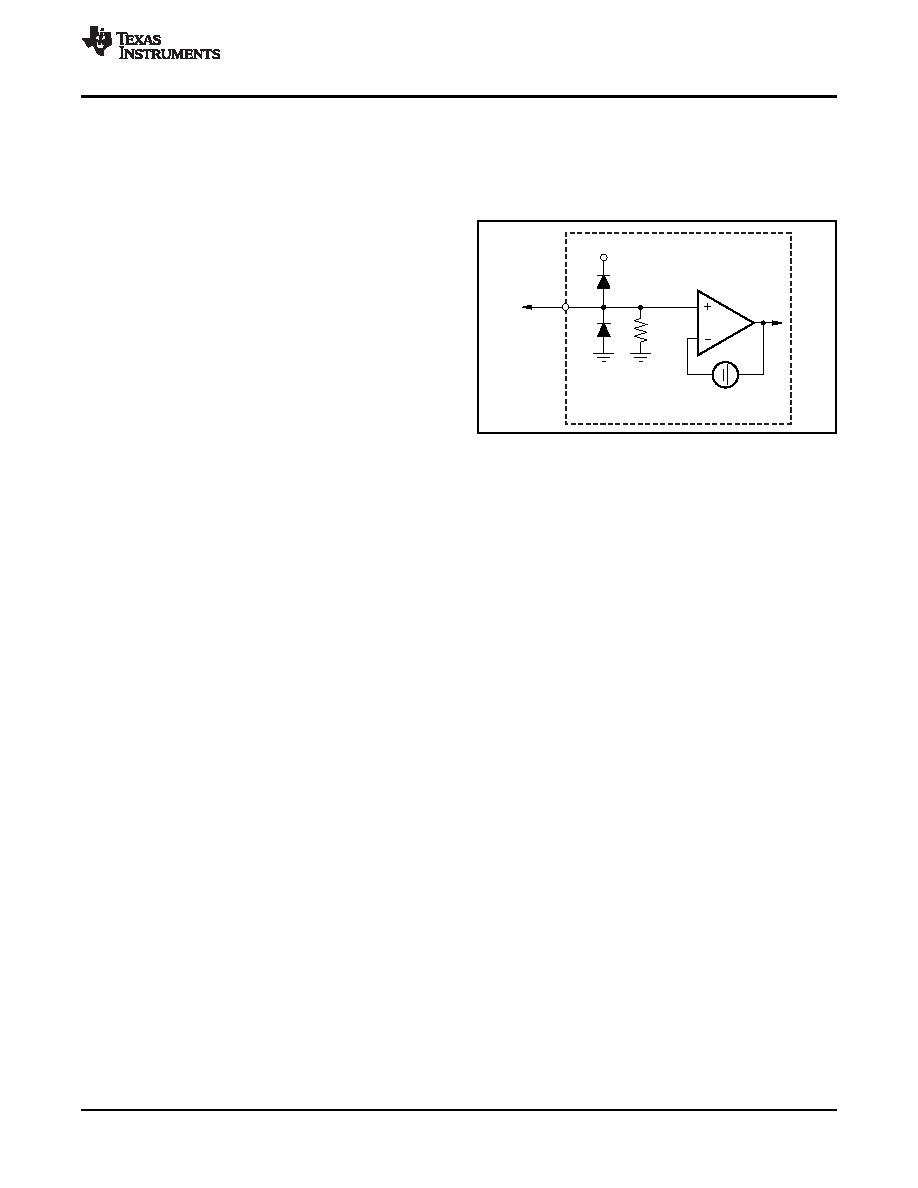
INPUT MODE OF OPERATION: DC
The input impedance of the THS7374 in this mode of
operation is dictated by the internal 800-k
pull-down
The
THS7374
allows
for
both
ac-coupled
and
resistor, as shown in Figure 58. Note that the internal
dc-coupled inputs. Many DACs or video encoders can
voltage shift does not appear at the input pin, but only
be dc-connected to the THS7374. One of the
the output pin. This configuration ensures there is no
drawbacks to dc coupling is when 0 V is applied to
issue with interfacing to the source.
the input. Although the input of the THS7374 allows
for a 0-V input signal with no issues, the output swing
of a traditional amplifier cannot yield a 0-V signal,
resulting in possible clipping. This condition is true for
any single-supply amplifier as a result of the output
transistor
limitations.
Both
CMOS
and
bipolar
transistors cannot go to 0 V while sinking current.
This characterization of a transistor is also the same
reason why the highest output voltage is always less
than the power-supply voltage when sourcing current.
This output clipping can reduce the sync amplitudes
(both horizontal and vertical sync) on the video
signal. A problem occurs if the receiver of this video
signal uses an AGC loop to account for losses in the
transmission line. Some video AGC circuits derive
Figure 58. Equivalent DC Input Mode Circuit
gain from the horizontal sync amplitude. If clipping
occurs on the sync amplitude, then the AGC circuit
can increase the gain too much—resulting in too
INPUT MODE OF OPERATION: AC SYNC TIP
much luma and/or chroma amplitude gain correction.
CLAMP
This overcorrection may result in a picture with an
Some video DACs or encoders are not referenced to
overly bright display with too much color saturation.
ground but rather to the positive power supply. The
Other AGC circuits use the chroma burst amplitude
resulting video signals are generally too high of a
for amplitude control, and a reduction in the sync
voltage for a dc-coupled video buffer to function
signals does not alter the proper gain setting.
properly. To account for this scenario, the THS7374
However, it is good engineering design practice to
incorporates a sync-tip clamp (STC) circuit. This
ensure that saturation/clipping does not take place.
function requires a capacitor (nominally 0.1 mF) to be
Transistors always take a finite amount of time to
in series with the input. Note that while the term
come out of saturation. This saturation could possibly
sync-tip-clamp is used throughout this document, it
result in timing delays or other aberrations on the
should be noted that the THS7374 would probably be
signals.
better termed to be a dc restoration circuit based on
how this function is performed. This circuit is an
To
eliminate
saturation/clipping
problems,
the
active clamp circuit and not a passive diode clamp
THS7374 has a 150-mV input level shift feature. This
function.
feature takes the input voltage and adds an internal
+150-mV shift to the signal. Since the THS7374 also
The input to the THS7374 has an internal control loop
has a gain of 6 dB (2 V/V), the resulting output with a
that sets the lowest input applied voltage to clamp at
0-V applied input signal is approximately 300 mV.
ground (0 V). By setting the reference at 0-V, the
The THS7374 rail-to-rail output stage can create this
THS7374 allows a dc-coupled input to also function.
output level while connected to a typical video load.
Therefore,
the
STC
is
considered
transparent
This feature ensures that no saturation/clipping of the
because it does not operate unless the input signal
sync signals occur. This shift is constant, regardless
goes below ground. The signal then goes through the
of the input signal. For example, if a 1-V input is
same 150-mV level shifter, resulting in an output
applied, the output is at 2.3 V.
voltage low level of 300 mV. If the input signal tries to
go below 0 V, the internal control loop of the
Because the internal gain is fixed at +6 dB, the gain
THS7374 sources up to 3-mA of current to increase
dictates what the allowable linear input voltage range
the input voltage level on the THS7374 input side of
can be without clipping concerns. For example, if the
the coupling capacitor. As soon as the voltage goes
power supply is set to 3.0 V, the maximum output is
above the 0-V level, the loop stops sourcing current
approximately 2.9 V while driving a significant amount
and becomes very high impedance.
of current. Thus, to avoid clipping, the allowable input
is [(2.9 V/2) – 0.15 V] = 1.3 V. This calculation is true
for up to the maximum recommended 5-V power
supply that allows about a [(4.9 V/2) – 0.15 V] = 2.3 V
input range while avoiding clipping on the output.
Copyright 2008–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
21
Product Folder Link(s): THS7374
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| THS7374IPWG4 | 4 CHANNEL, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO14 |
| THS7374IPWRG4 | 4 CHANNEL, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO14 |
| THS7375IPWR | VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO14 |
| THS7375IPW | VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO14 |
| THS7375IPWG4 | VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO14 |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| THS7374IPW | 制造商:Texas Instruments 功能描述:Video Buffer / Amplifier IC 制造商:Texas Instruments 功能描述:IC, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, QUAD 9.5MHZ TSSOP14 |
| THS7374IPWG4 | 功能描述:視頻放大器 4-Ch SDTV Video Amp RoHS:否 制造商:ON Semiconductor 通道數(shù)量:4 電源類型: 工作電源電壓:3.3 V, 5 V 電源電流: 最小工作溫度: 最大工作溫度: 封裝 / 箱體:TSSOP-14 封裝:Reel |
| THS7374IPWR | 功能描述:視頻放大器 4-Ch SDTV Component & Composite Vid Amp RoHS:否 制造商:ON Semiconductor 通道數(shù)量:4 電源類型: 工作電源電壓:3.3 V, 5 V 電源電流: 最小工作溫度: 最大工作溫度: 封裝 / 箱體:TSSOP-14 封裝:Reel |
| THS7374IPWRG4 | 功能描述:視頻放大器 4-Ch SDTV Video Amp RoHS:否 制造商:ON Semiconductor 通道數(shù)量:4 電源類型: 工作電源電壓:3.3 V, 5 V 電源電流: 最小工作溫度: 最大工作溫度: 封裝 / 箱體:TSSOP-14 封裝:Reel |
| THS7375 | 制造商:TI 制造商全稱:Texas Instruments 功能描述:4-Channel SDTV Video Amplifier with 6th-Order Filters and 5.6-V/V Gain |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。