- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買(mǎi)賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄382332 > MM74HC191J (NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR CORP) MM54HC190/MM74HC190 Synchronous Decade Up/Down Counters with Mode Control MM54HC191/MM74HC191 Synchronous Binary Up/Down Counters with Mode Control PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | MM74HC191J |
| 廠商: | NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR CORP |
| 元件分類: | 通用總線功能 |
| 英文描述: | MM54HC190/MM74HC190 Synchronous Decade Up/Down Counters with Mode Control MM54HC191/MM74HC191 Synchronous Binary Up/Down Counters with Mode Control |
| 中文描述: | HC/UH SERIES, SYN POSITIVE EDGE TRIGGERED 4-BIT BIDIRECTIONAL BINARY COUNTER, CDIP16 |
| 封裝: | CERAMIC, DIP-16 |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 1/8頁(yè) |
| 文件大小: | 202K |
| 代理商: | MM74HC191J |
TL/F/5322
M
January 1988
MM54HC190/MM74HC190 Synchronous
Decade Up/Down Counters with Mode
Control MM54HC191/MM74HC191
Synchronous Binary Up/Down Counters
with Mode Control
General Description
These high speed synchronous counters utilize advanced
silicon-gate CMOS technology. They possess the high noise
immunity and low power consumption of CMOS technology,
along with the speeds of low power Schottky TTL.
These circuits are synchronous, reversible, up/down count-
ers. The MM54HC191/MM74HC191 are 4-bit binary count-
ers and the MM54HC190/MM74HC190 are BCD counters.
Synchronous operation is provided by having all flip-flops
clocked simultaneously, so that the outputs change simulta-
neously when so instructed by the steering logic. This mode
of operation eliminates the output counting spikes normally
associated with asynchronous (ripple clock) counters.
The outputs of the four master-slave flip-flops are triggered
on a low-to-high level transition of the clock input, if the
enable input is low. A high at the enable input inhibits count-
ing. The direction of the count is determined by the level of
the down/up input. When low, the counter counts up and
when high, it counts down.
These counters are fully programmable; that is, the outputs
may be preset to either level by placing a low on the load
input and entering the desired data at the data inputs. The
output will change independent of the level of the clock in-
put. This feature allows the counters to be used as modulo-
N dividers by simply modifying the count length with the
preset inputs.
Two outputs have been made available to perform the cas-
cading function: ripple clock and maximum/minimum count.
The latter output produces a high-level output pulse with a
duration approximately equal to one complete cycle of the
clock when the counter overflows or underflows. The ripple
clock output produces a low-level output pulse equal in
width to the low-level portion of the clock input when an
overflow or underflow condition exists. The counters can be
easily cascaded by feeding the ripple clock output to the
enable input of the succeeding counter if parallel clocking is
used, or to the clock input if parallel enabling is used. The
maximum/minimum count output can be used to accom-
plish look-ahead for high-speed operation.
Features
Y
Level changes on Enable or Down/Up can be made re-
gardless of the level of the clock input
Y
Wide power supply range: 2–6V
Y
Low quiescent supply current: 80
m
A maximum
(74HC Series)
Y
Low input current: 1
m
A maximum
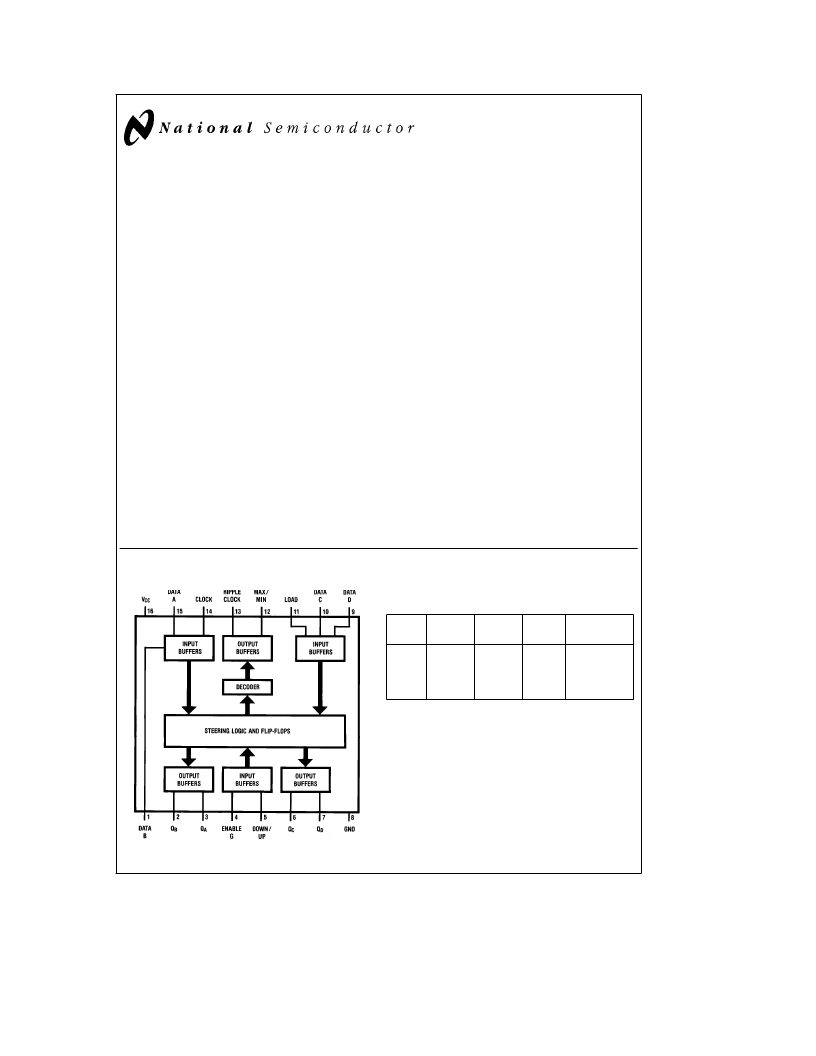
Connection Diagram
Dual-In-Line Package
TL/F/5322–1
Top View
Load
Enable
G
Down/
Up
Clock
Function
H
H
L
H
L
L
X
H
L
H
X
X
u
u
X
X
Count Up
Count Down
Load
No Change
Asynchronous inputs Low input to load sets Q
A
e
A,
Q
B
e
B, Q
C
e
C, and Q
D
e
D
Order Number MM54HC190/191 or MM74HC190/191
C
1995 National Semiconductor Corporation
RRD-B30M105/Printed in U. S. A.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MM74HC191N | MM54HC190/MM74HC190 Synchronous Decade Up/Down Counters with Mode Control MM54HC191/MM74HC191 Synchronous Binary Up/Down Counters with Mode Control |
| MM54HC245A | Octal TRI-STATE Transceiver |
| MM54HC253 | Dual 4-Channel TRI-STATE Multiplexer |
| MM54HC253J | Dual 4-Channel TRI-STATE Multiplexer |
| MM74HC253 | Dual 4-Channel TRI-STATE Multiplexer |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| MM74HC191N | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:- Bulk |
| MM74HC191WMX | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:- Bulk 制造商:Texas Instruments 功能描述: |
| MM74HC192 | 制造商:NSC 制造商全稱:National Semiconductor 功能描述:Synchronous Decade Up/Down Counters Synchronous Binary Up/Down Counters |
| MM74HC193 | 制造商:NSC 制造商全稱:National Semiconductor 功能描述:Synchronous Decade Up/Down Counters Synchronous Binary Up/Down Counters |
| MM74HC193J | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:- Bulk |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。