- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄383359 > MAX3202EETT (MAXIM INTEGRATED PRODUCTS INC) Dual LVDS Receiver with -2 to 4.4V Common-mode Range 8-SOIC -40 to 85 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | MAX3202EETT |
| 廠商: | MAXIM INTEGRATED PRODUCTS INC |
| 元件分類: | 參考電壓二極管 |
| 英文描述: | Dual LVDS Receiver with -2 to 4.4V Common-mode Range 8-SOIC -40 to 85 |
| 中文描述: | UNIDIRECTIONAL, 4 ELEMENT, SILICON, TVS DIODE, MO-229WEEA |
| 封裝: | 3 X 3 MM, 0.80 MM HEIGHT, QFN-6 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 6/15頁 |
| 文件大小: | 754K |
| 代理商: | MAX3202EETT |
M
IEC 61000-4-2
The IEC 61000-4-2 standard covers ESD testing and
performance of finished equipment. The MAX3202E/
MAX3203E/MAX3204E/MAX3206E help users design
equipment that meets Level 4 of IEC 61000-4-2.
The main difference between tests done using the
Human Body Model and IEC 61000-4-2 is higher peak
current in IEC 61000-4-2. Because series resistance is
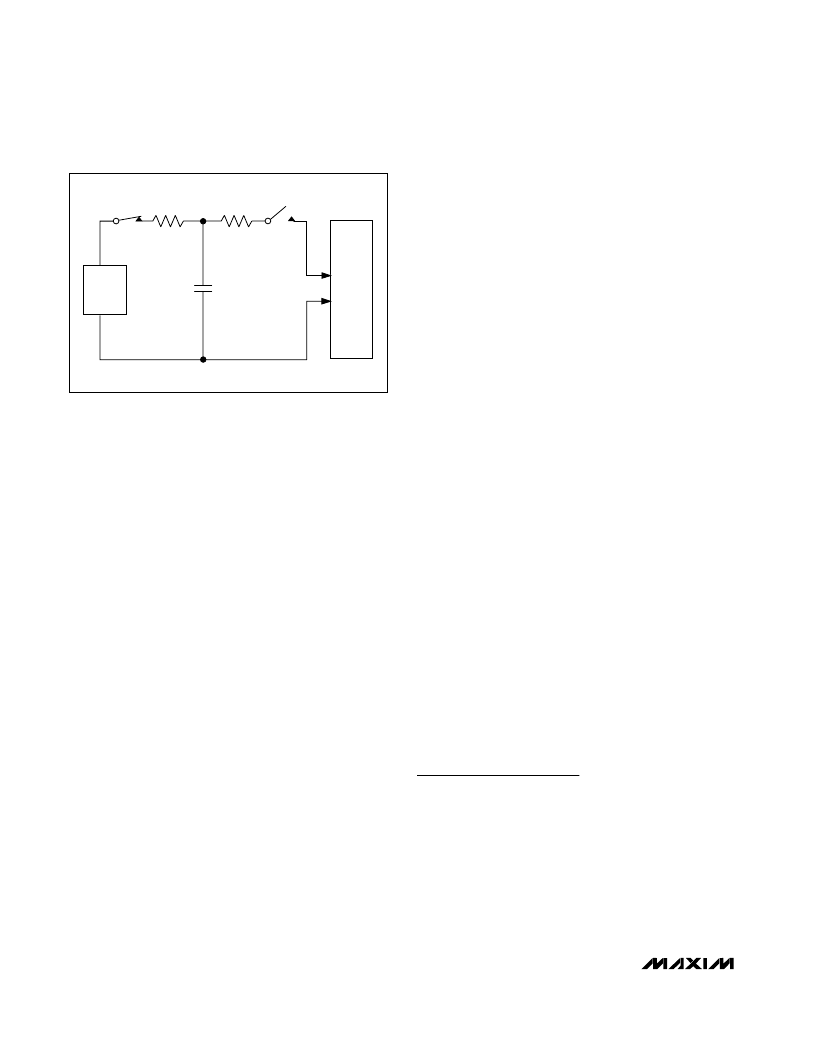
lower in the IEC 61000-4-2 ESD test model (Figure 6)
the ESD-withstand voltage measured to this standard is
generally lower than that measured using the Human
Body Model. Figure 3 shows the current waveform for
the ±8kV IEC 61000-4-2 Level 4 ESD Contact
Discharge test.
The Air-Gap Discharge test involves approaching the
device with a charged probe. The Contact Discharge
method connects the probe to the device before the
probe is energized.
Layout Recommendations
Proper circuit-board layout is critical to suppress ESD-
induced line transients. The MAX3202E/MAX3203E/
MAX3204E/MAX3206E clamp to 100V; however, with
improper layout, the voltage spike at the device is
much higher. A lead inductance of 10nH with a 45A
current spike at a dv/dt of 1ns results in an
ADDITION-
AL
450V spike on the protected line. It is
essential
that
the layout of the PC board follows these guidelines:
1) Minimize trace length between the connector or
input terminal, I/O_, and the protected signal line.
2) Use separate planes for power and ground to reduce
parasitic inductance and to reduce the impedance to
the power rails for shunted ESD current.
3) Ensure short ESD transient return paths to GND
and V
CC
.
4) Minimize conductive power and ground loops.
5) Do not place critical signals near the edge of the
PC board.
6) Bypass V
CC
to GND with a low-ESR ceramic capac-
itor as close to V
CC
as possible.
7) Bypass the supply of the protected device to GND
with a low-ESR ceramic capacitor as close to the
supply pin as possible.
UCSP Considerations
For general UCSP package information and PC layout
considerations, refer to Maxim Application Note 263,
Wafer-Level Chip-Scale Package
.
___________________UCSP Reliability
The UCSP represents a unique packaging form factor
that may not perform equally to a packaged product
through traditional mechanical reliability tests. UCSP
reliability is integrally linked to the user’s assembly meth-
ods, circuit-board material, and usage environment.
The user should closely review these areas when con-
sidering use of a UCSP. Performance through operat-
ing life test and moisture resistance remains
uncompromised as it is primarily determined by the
wafer-fabrication process. Mechanical stress perfor-
mance is a greater consideration for a UCSP. UCSPs
are attached through direct solder contact to the user’s
PC board, foregoing the inherent stress relief of a pack-
aged product lead frame. Solder-joint contact integrity
must be considered. Table 1 shows the testing done to
characterize the UCSP reliability performance. In con-
clusion, the UCSP is capable of performing reliably
through environmental stresses as indicated by the
results in the table. Additional usage data and recom-
mendations are detailed in the UCSP application note,
which can be found on Maxim’s website at
www.maxim-ic.com.
Chip Information
DIODE COUNT:
MAX3202E: 4
MAX3203E: 6
MAX3204E: 8
MAX3206E: 12
PROCESS: BiCMOS
Low-Capacitance, 2/3/4/6-Channel, ±15kV ESD
Protection Arrays for High-Speed Data Interfaces
6
_______________________________________________________________________________________
CHARGE-CURRENT-
LIMIT RESISTOR
DISCHARGE
RESISTANCE
STORAGE
CAPACITOR
Cs
150pF
R
C
50
to 100
R
D
330
HIGH-
VOLTAGE
DC
SOURCE
DEVICE
UNDER
TEST
Figure 6. IEC 61000-4-2 ESD Test Model
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MAX3203EETT | Dual LVDS Receiver with -2 to 4.4V Common-mode Range 8-SOIC -40 to 85 |
| MAX3204EETT | Dual LVDS Receiver with -2 to 4.4V Common-mode Range 8-SOIC -40 to 85 |
| MAX3212CAI | 5V High-Speed RS-232 Transceivers with 0.1uF Capacitors |
| MAX3212EWI | 5V High-Speed RS-232 Transceivers with 0.1uF Capacitors |
| MAX3212CWI | 5V High-Speed RS-232 Transceivers with 0.1uF Capacitors |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| MAX3202EET-T | 功能描述:TVS二極管陣列 RoHS:否 制造商:Littelfuse 極性: 通道:4 Channels 擊穿電壓: 鉗位電壓:11.5 V 工作電壓:2.5 V 峰值浪涌電流:20 A 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 端接類型:SMD/SMT 系列: 最小工作溫度:- 40 C 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C |
| MAX3202EETT+ | 制造商:Maxim Integrated Products 功能描述:LOW CAPACITANCE 2/3/4/6 CH 15KV ESD PROT ARYS 6TDFN EP - Rail/Tube |
| MAX3202EETT+T | 功能描述:TVS二極管陣列 2Ch ESD Protection Array RoHS:否 制造商:Littelfuse 極性: 通道:4 Channels 擊穿電壓: 鉗位電壓:11.5 V 工作電壓:2.5 V 峰值浪涌電流:20 A 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 端接類型:SMD/SMT 系列: 最小工作溫度:- 40 C 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C |
| MAX3202EETT-T | 功能描述:TVS二極管陣列 2Ch ESD Protection Array RoHS:否 制造商:Littelfuse 極性: 通道:4 Channels 擊穿電壓: 鉗位電壓:11.5 V 工作電壓:2.5 V 峰值浪涌電流:20 A 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 端接類型:SMD/SMT 系列: 最小工作溫度:- 40 C 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C |
| MAX3202EEWS+ | 制造商:Maxim Integrated Products 功能描述:LOW-CAPACITANCE 2/6-CHANNEL +/-15 - Rail/Tube |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。