- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄383058 > HIP6302 (Intersil Corporation) Microprocessor CORE Voltage Regulator Multi-Phase Buck PWM Controller(微處理器核心多相脈寬調(diào)制解調(diào)器) PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | HIP6302 |
| 廠商: | Intersil Corporation |
| 英文描述: | Microprocessor CORE Voltage Regulator Multi-Phase Buck PWM Controller(微處理器核心多相脈寬調(diào)制解調(diào)器) |
| 中文描述: | 微處理器核心電壓調(diào)節(jié)器的多相降壓PWM控制器(微處理器核心多相脈寬調(diào)制解調(diào)器) |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 14/17頁(yè) |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 184K |
| 代理商: | HIP6302 |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)當(dāng)前第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)
14
The critical small components include the bypass capacitors
for VCC and PVCC on the gate driver ICs. Locate the
bypass capacitor, C
BP
, for the HIP6302 controller close to
the device. It is especially important to locate the resistors
associated with the input to the amplifiers close to their
respective pins, since they represent the input to feedback
amplifiers. Resistor R
T
, that sets the oscillator frequency
should also be located next to the associated pin. It is
especially important to place the R
SEN
resistor(s) at the
respective terminals of the HIP6302.
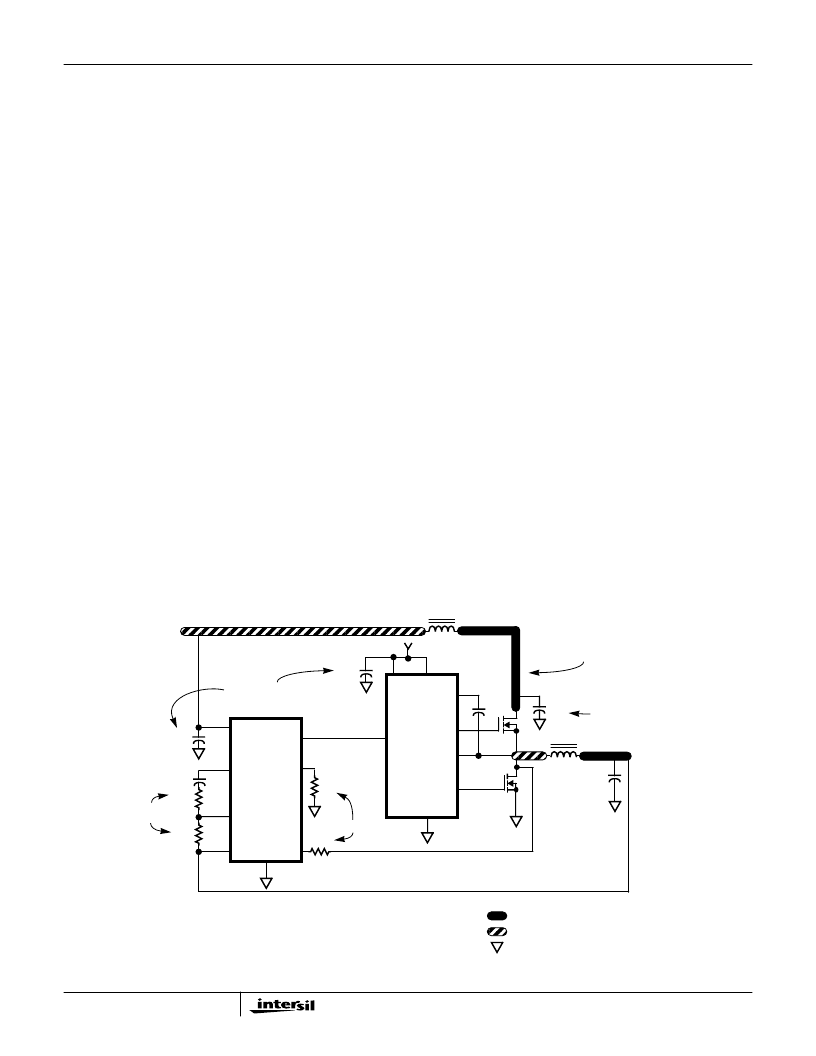
A multi-layer printed circuit board is recommended. Figure 11
shows the connections of the critical components for one
output channel of the converter. Note that capacitors C
IN
and
C
OUT
could each represent numerous physical capacitors.
Dedicate one solid layer, usually the middle layer of the PC
board, for a ground plane and make all critical component
ground connections with vias to this layer. Dedicate another
solid layer as a power plane and break this plane into smaller
islands of common voltage levels. Keep the metal runs from
the PHASE terminal to inductor L
O1
short. The power plane
should support the input power and output power nodes. Use
copper filled polygons on the top and bottom circuit layers for
the phase nodes. Use the remaining printed circuit layers for
small signal wiring. The wiring traces from the driver IC to the
MOSFET gate and source should be sized to carry at least
one ampere of current.
Component Selection Guidelines
Output Capacitor Selection
The output capacitor is selected to meet both the dynamic
load requirements and the voltage ripple requirements. The
load transient for the microprocessor CORE is characterized
by high slew rate (di/dt) current demands. In general,
multiple high quality capacitors of different size and dielectric
are paralleled to meet the design constraints.
Modern microprocessors produce severe transient load rates.
High frequency capacitors supply the initially transient current
and slow the load rate-of-change seen by the bulk capacitors.
The bulk filter capacitor values are generally determined by
the ESR (effective series resistance) and voltage rating
requirements rather than actual capacitance requirements.
High frequency decoupling capacitors should be placed as
close to the power pins of the load as physically possible. Be
careful not to add inductance in the circuit board wiring that
could cancel the usefulness of these low inductance
components. Consult with the manufacturer of the load on
specific decoupling requirements.
Use only specialized low-ESR capacitors intended for
switching-regulator applications for the bulk capacitors. The
bulk capacitor’s ESR determines the output ripple voltage
and the initial voltage drop following a high slew-rate
transient’s edge. In most cases, multiple capacitors of small
case size perform better than a single large case capacitor.
Bulk capacitor choices include aluminum electrolytic, OS-
Con, Tantalum and even ceramic dielectrics. An aluminum
electrolytic capacitor’s ESR value is related to the case size
with lower ESR available in larger case sizes. However, the
equivalent series inductance (ESL) of these capacitors
increases with case size and can reduce the usefulness of
the capacitor to high slew-rate transient loading.
Unfortunately, ESL is not a specified parameter. Consult the
capacitor manufacturer and measure the capacitor’s
impedance with frequency to select a suitable component.
V
CORE
+12V
VIA CONNECTION TO GROUND PLANE
ISLAND ON POWER PLANE LAYER
ISLAND ON CIRCUIT PLANE LAYER
L
O1
C
OUT
C
IN
+5V
IN
KEY
PHASE
VCC
USE INDIVIDUAL METAL RUNS
FOR EACH CHANNEL TO HELP
COMP
HIP6302
PWM
R
T
R
IN
R
FB
C
BP
FB
VSEN
ISEN
R
SEN
HIP6601
C
BOOT
C
BP
C
T
V
CC
FS/DIS
PVCC
LOCATE NEXT TO IC PIN
LOCATE NEXT
TO FB PIN
LOCATE NEXT TO IC PIN(S)
ISOLATE OUTPUT STAGES
LOCATE NEAR TRANSISTOR
FIGURE 11. PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD POWER PLANES AND ISLANDS
HIP6302
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| HIP6302CB | Microprocessor CORE Voltage Regulator Multi-Phase Buck PWM Controller |
| HIP6302VCB | Microprocessor CORE Voltage Regulator Multi-Phase Buck PWM Controller |
| HIP6302VCB-T | Microprocessor CORE Voltage Regulator Multi-Phase Buck PWM Controller |
| HIP6302VCBZ | 150000 SYSTEM GATE 2.5 VOLT FPGA - NOT RECOMMENDED for NEW DESIGN |
| HIP6302VCBZ-T | 150000 SYSTEM GATE 2.5 VOLT FPGA - NOT RECOMMENDED for NEW DESIGN |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| HIP6302_04 | 制造商:INTERSIL 制造商全稱:Intersil Corporation 功能描述:Microprocessor CORE Voltage Regulator Multi-Phase Buck PWM Controller |
| HIP6302CB | 功能描述:IC REG CTRLR BUCK PWM 16-SOIC RoHS:否 類別:集成電路 (IC) >> PMIC - 穩(wěn)壓器 - DC DC 切換控制器 系列:- 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)包裝:4,000 系列:- PWM 型:電壓模式 輸出數(shù):1 頻率 - 最大:1.5MHz 占空比:66.7% 電源電壓:4.75 V ~ 5.25 V 降壓:是 升壓:無(wú) 回掃:無(wú) 反相:無(wú) 倍增器:無(wú) 除法器:無(wú) Cuk:無(wú) 隔離:無(wú) 工作溫度:-40°C ~ 85°C 封裝/外殼:40-VFQFN 裸露焊盤(pán) 包裝:帶卷 (TR) |
| HIP6302CB-T | 功能描述:電流型 PWM 控制器 MPU CORE Volt Reg RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 開(kāi)關(guān)頻率:27 KHz 上升時(shí)間: 下降時(shí)間: 工作電源電壓:6 V to 15 V 工作電源電流:1.5 mA 輸出端數(shù)量:1 最大工作溫度:+ 105 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:TSSOP-14 |
| HIP6302CB-TS2495 | 制造商:Intersil Corporation 功能描述:SWITCHING CONTROLLER, 1500 kHz SWITCHING FREQ-MAX, PDSO16 |
| HIP6302CBZ | 功能描述:電流型 PWM 控制器 VER OF HIP6302CB RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 開(kāi)關(guān)頻率:27 KHz 上升時(shí)間: 下降時(shí)間: 工作電源電壓:6 V to 15 V 工作電源電流:1.5 mA 輸出端數(shù)量:1 最大工作溫度:+ 105 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:TSSOP-14 |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。