- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網 > PDF目錄371775 > HC55143 (Intersil Corporation) Low Power Universal SLIC Family PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | HC55143 |
| 廠商: | Intersil Corporation |
| 英文描述: | Low Power Universal SLIC Family |
| 中文描述: | 低功耗通用用戶接口家庭 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 17/35頁 |
| 文件大小: | 382K |
| 代理商: | HC55143 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁當前第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁
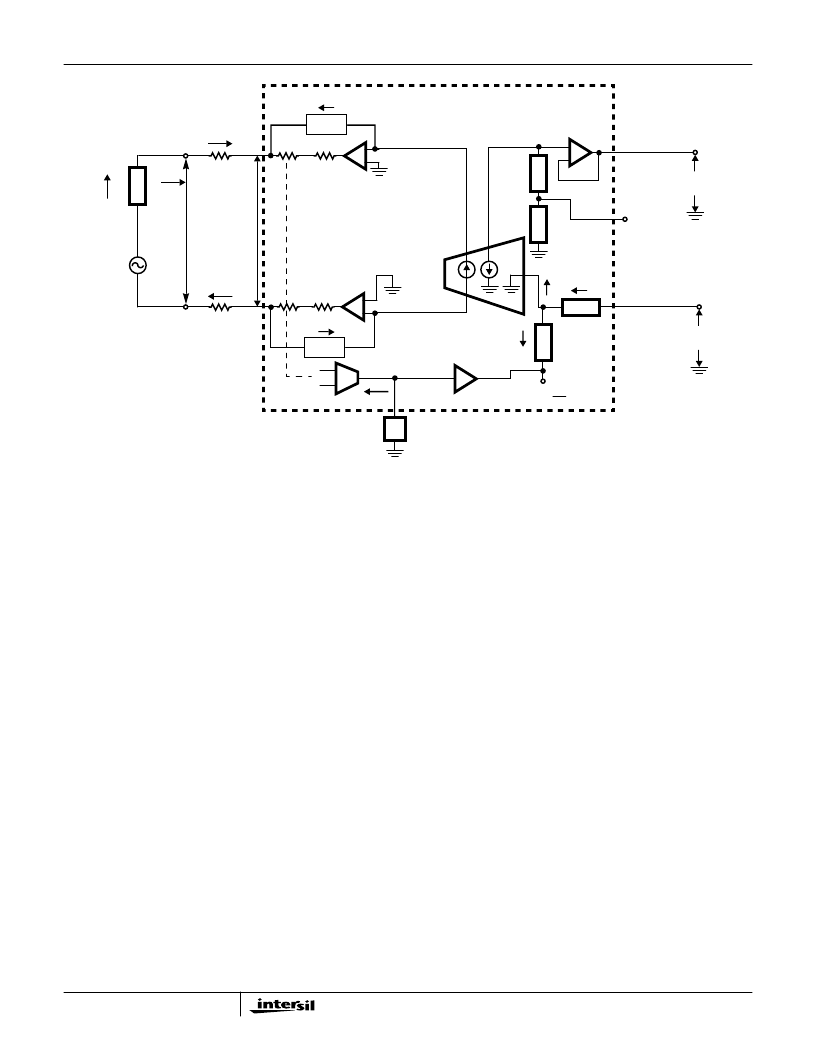
4-17
(AC) 2-Wire to 4-Wire Gain
The 2-wire to 4-wire gain is equal to V
TX
/E
G
with V
RX
= 0
From Equation 18 with V
RX
= 0
V
TX
′
Substituting Equation 24 into Equation 23 and simplifying.
By design, VTX = -VTX′, therefore
V
G
A more useful form of the equation is rewritten in terms of
V
TX
/V
TR
. A voltage divider equation is written to convert
from E
G
to V
TR
as shown in Equation 27.
Z
TR
Rearranging Equation 27 in terms of E
G
, and substituting
into Equation 26 results in an equation for 2-wire to 4-wire
gain that’s a function of the synthesized input impedance of
the SLIC (Z
TR
) and the protection resistors (R
P
).
Notice that the phase of the 2-wire to 4-wire signal is in
phase with the input signal.
(AC) 4-Wire to 4-Wire Gain
The 4-wire to 4-wire gain is equal to V
TX
/V
RX
, E
G
= 0.
From Equation 18.
Substituting -V
TR
/Z
L
into Equation 29 for I
M
results in
Equation 30.
Substituting Equation 21 for V
TR
in Equation 30 and
simplifying results in Equation 31.
(AC) 2-Wire Impedance
The AC 2-wire impedance (Z
TR
) is the impedance looking
into the SLIC, including the fuse resistors. The formula to
calculate the proper Z
T
for matching the 2-wire impedance is
shown in Equation 32.
Equation 32 can now be used to match the SLIC’s
impedance to any known line impedance (Z
TR
).
V
TX
V
RX
TIP
RING
Z
TR
V
TR
E
G
-
V
TX
′
I
M
V
TX
UniSLIC14
R
P
R
P
+
-
+
-
+
-
+
V
RX
+
-
I
M
Z
L
FIGURE 17. SIMPLIFIED AC TRANSMISSION CIRCUIT
+
500K
R
S
+
-
500K
R
S
Z
T
500K
500K
500K
500K
PTG
+
-
I
X
V
A
= I
M
(Z
TR
-2R
P
)
2
I
X
I
X
+
-
I
X
+
-
5
+
-
+
-
I
M
+
-
20
20
1/80K
= 200 (Z
TR
- 2R
P
)
A = 1
I
X
I
R
INT
20
R
INT
20
E
–
G
Z
L
I
M
2R
P
I
M
V
TX
′
–
+
+
0
=
Loop Equation
(EQ. 23)
I
M
Z
TR
2R
P
–
(
)
–
=
(EQ. 24)
E
G
I
M
Z
L
Z
TR
+
(
)
=
(EQ. 25)
G
2-4
=
----------
=
I
Z
M
L
2R
TR
–
(
)
)
-------------------+
Z
L
2R
TR
–
(
-------------+
)
)
=
(EQ. 26)
V
TR
=
L
-------------+
E
G
(EQ. 27)
G
2-4
=
V
TR
----------
=
Z
- 2R
P
TR
-----------------------------
(EQ. 28)
V
TX
′
V
–
TX
2
–
V
RX
I
M
Z
TR
2R
P
–
(
)
+
=
=
(EQ. 29)
V
TX
2
–
V
RX
V
Z
---------------------------------------------
2R
–
(
)
L
–
=
(EQ. 30)
G
4
4
–
V
RX
-----------
2
–
Z
+ 2R
P
L
TR
-------+
=
=
(EQ. 31)
Z
T
200
Z
TR
2R
P
–
(
)
=
(EQ. 32)
HC55120, HC55121, HC55130, HC55131, HC55140, HC55141, HC55142, HC55143, HC55150, HC55151
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| HC55143IM | Low Power Universal SLIC Family |
| HC55150 | Low Power Universal SLIC Family |
| HC55150CB | Low Power Universal SLIC Family |
| HC55150CM | Low Power Universal SLIC Family |
| HC55151 | Low Power Universal SLIC Family |
相關代理商/技術參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| HC55143IM | 功能描述:IC SLIC UNIVERSAL LP 32-PLCC RoHS:否 類別:集成電路 (IC) >> 接口 - 電信 系列:UniSLIC14 產品培訓模塊:Lead (SnPb) Finish for COTS 產品變化通告:Product Discontinuation 06/Feb/2012 標準包裝:750 系列:* |
| HC5514X | 制造商:Harris Corporation 功能描述: |
| HC5514XB | 制造商:Harris Corporation 功能描述: |
| HC5514XEVAL1 | 功能描述:界面開發(fā)工具 UNISLIC14 FAMILY EVALUATION BRD RoHS:否 制造商:Bourns 產品:Evaluation Boards 類型:RS-485 工具用于評估:ADM3485E 接口類型:RS-485 工作電源電壓:3.3 V |
| HC5514XEVAL2 | 功能描述:界面開發(fā)工具 EVALRD TO GO W/IDT MOTHER BRD RoHS:否 制造商:Bourns 產品:Evaluation Boards 類型:RS-485 工具用于評估:ADM3485E 接口類型:RS-485 工作電源電壓:3.3 V |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。